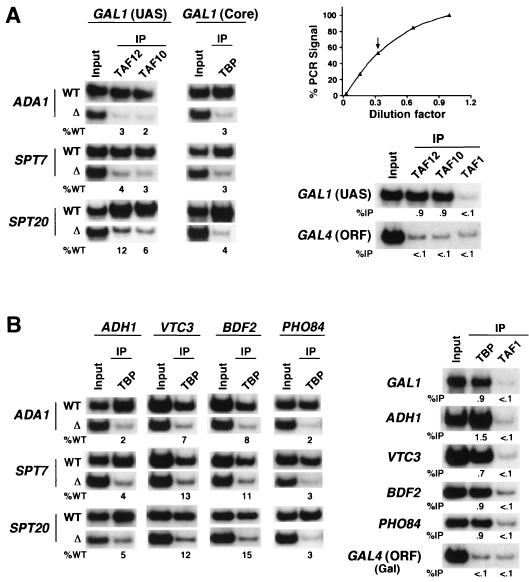
FIG. 2.
General requirement of Ada1p, Spt7p, and Spt20p for recruitment of TBP to SAGA-dependent promoters. (A) Wild-type (WT), ada1Δ, spt7Δ, and spt20Δ strains were first grown in glucose-containing medium (YPD) and then shifted to galactose-containing medium (YPG) 5 h prior to treatment with formaldehyde. Formaldehyde-based in vivo cross-linking and ChIP were carried out as previously described (28). Immunoprecipitation assays were performed with polyclonal antibodies against TAF10, TAF12, or TBP. TAF10 and TAF12 are representative SAGA components used to monitor recruitment of the SAGA complex. Primer pairs located in the GAL1 UAS or core promoter were used for PCR analysis of the input and immunoprecipitated (IP) DNA samples. All PCRs were carried out in the linear range of DNA amplification, as indicated by the arrow in the curve shown in the top right panel. The percentage of DNA immunoprecipitated relative to that of the wild type (%WT) is indicated. Background levels in the immunoprecipitation assay are shown by using an irrelevant DNA sequence (GAL4 ORF [open reading frame]) and an irrelevant antibody control (TAF1 is a specific component of the TFIID complex, which is not associated with the core promoters of the genes analyzed) which immunoprecipitated less than 0.1% of DNA. (B) All strains were grown in YPD to an OD600 of 1.0 prior to formaldehyde treatment. Analysis of TBP binding to the core promoters of ADH1, VTC3, BDF2, and PHO84 was performed as described for panel A. The background signal obtained with the irrelevant anti-TAF1 antibody control is shown on the right.