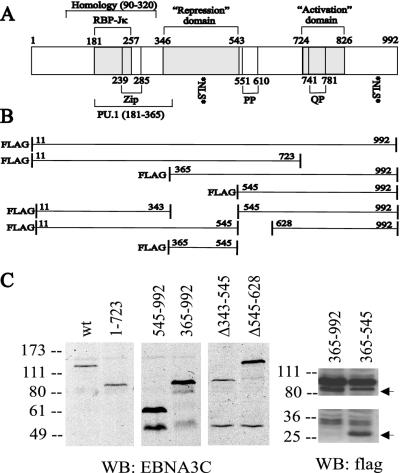
FIG. 1.
Schematic diagram of wild-type EBNA-3C and deletion mutants used in these experiments. (A) aa 90 to 320 have the highest level of identity (22 to 27%) among the EBNA-3 proteins. The RBP-Jκ-binding site (aa 181 to 257), a PU.1-binding region (aa 181 to 365) (64), and a putative leucine zipper (aa 239 to 285) are indicated. The repression (aa 346 to 543) and activation (aa 724 to 826) domains were defined based on their effects on a Gal4-responsive promoter when fused to the Gal4 DBD (3, 31). Repeats containing prolines (PP) and glutamine-proline residues (QP) are noted, as are two potential nuclear localization signal sequences (NLS). (B) EBNA-3C deletion constructs utilized in this study. (C) Immunoblots of lysates from 12 million BJAB cells that had been transfected 40 to 48 h previously with 1 μg of pSG5 expression vector for the indicated EBNA-3C deletion construct. The left panel used the EBNA-3C-specific A10 monoclonal antibody, while the right panel used M2 and M5 monoclonal antibodies against the Flag epitope tag. The top arrow indicates the position of Flag-EBNA-3C aa 363 to 992, which migrates just below a background band present in both lanes, and the bottom arrow indicates the position of Flag-EBNA-3C aa 365 to 545. WB, Western blot; wt, wild type.