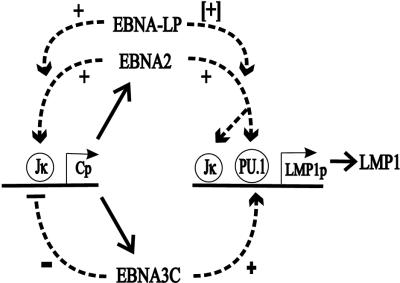
FIG. 8.
Proposed roles of EBNA-3C in regulating EBNA-2 transactivation activity in EBV-infected B lymphocytes. The Wp EBNA promoter directs initial transcription of EBNA-2 and EBNA-LP mRNAs, which are polyadenylated at a site downstream of the EBNA-2 ORF. EBNA-2 activates the Cp promoter and probably also up-regulates the Wp promoter, resulting in higher-level transcription through EBNA-LP and EBNA-2 and transcription of EBNA-3A, EBNA-3B, EBNA-3C, and EBNA-1 mRNAs. EBNA-2, EBNA-LP, and EBNA-3C collaborate to coactivate the LMP1 promoter and to sustain LMP1 expression at the appropriate level under all conditions of cell growth. LMP1 has a key role in LCL transformation, growth, and survival. EBNA-2, EBNA-LP, and EBNA-3C could cause runaway positive feedback up-regulation of the EBNA Cp and Wp promoters, but EBNA-3C, EBNA-3A, and EBNA-3B all contribute to repressing EBNA-2 and EBNA-LP coactivation of these promoters. Similar effects of EBNA-2, EBNA-LP, EBNA-3C, EBNA-3A, and EBNA-3B are presumed to govern transcription at other viral and cell promoters in latent EBV infection.