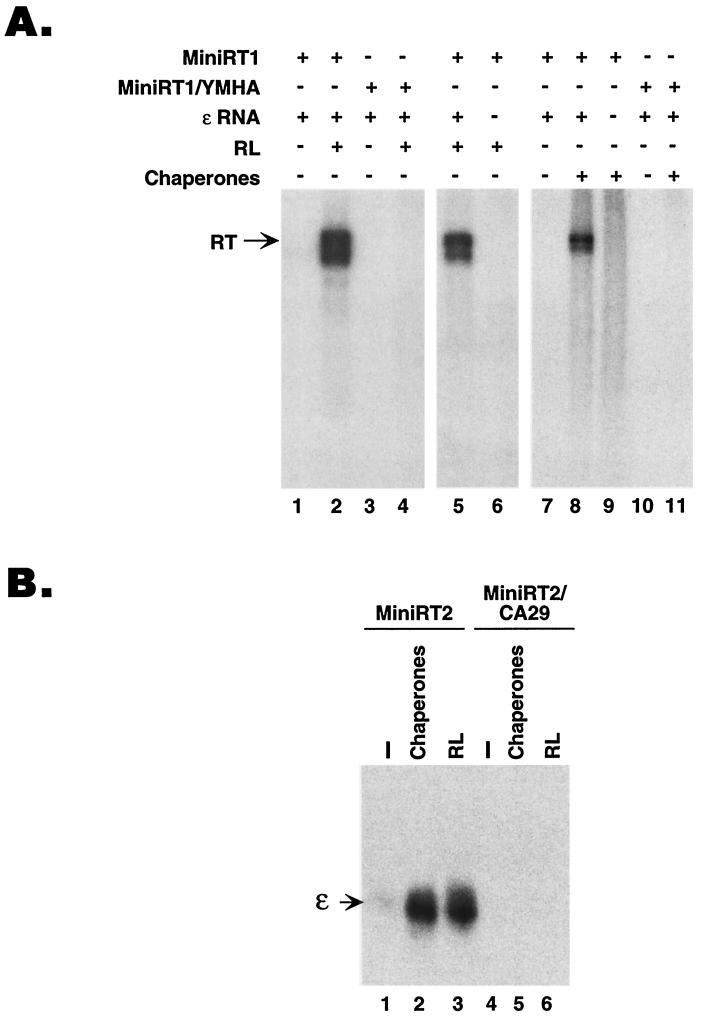
FIG. 4.
Reconstitution of protein priming and RT-ɛ interaction required RT functions and the ɛ RNA. (A) GST-MiniRT1 or its mutant derivative MiniRT1/YMHA, which harbors two amino acid substitutions in the RT active site, abolishing its catalytic activity, was used in the in vitro protein-priming assay. Reconstitution was done using either reticulocyte lysate (RL) or the five chaperone proteins (Hsp90, Hsp70, Hop, Ydj1, and p23). Where indicated, the ɛ RNA was omitted from some of the reactions shown. (B) Purified GST-MiniRT2 or its mutant derivative MiniRT2/CA29, which harbors two amino acid substitutions abolishing its ɛ RNA binding activity, was assessed for ɛ binding activity by the GST pull-down assay (see Materials and Methods). The minimal RT proteins were prebound to the glutathione beads, and 32P-labeled ɛ RNA was then allowed to bind to the RT proteins with (lanes 1 and 4) or without the addition of the five chaperones proteins (Hsp90, hsp70, Hop, Ydj1, and p23; lanes 2 and 5) or RL (lanes 3 and 6). All reactions were supplemented with the ATP regenerating system. The bound ɛ RNA was then resolved by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. The ɛ RNA is indicated.