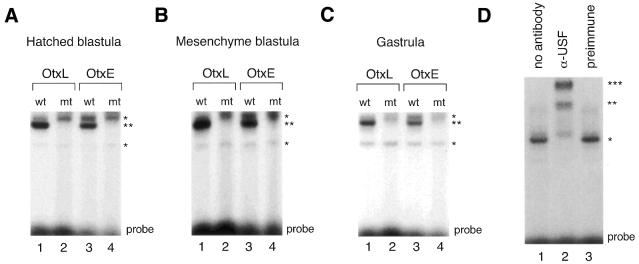
Figure 6.
E-box binding activities detected in stage-specific nuclear extracts. (A) Gel mobility shift analysis was performed using nuclear extracts (2 µg) prepared from embryos at the hatched blastula stage and double-stranded oligonucleotide extending either from base pairs –229 to –208 of the HpOtxL promoter (OtxL) or from base pairs –75 to –54 of the HpOtxE promoter (OtxE) as probe. ‘wt’ and ‘mt’ indicate wild-type and mutant probes, respectively; the latter probe contains the mutant AAGCTT sequence while the former probe contains the wild-type CACGTG sequence. The positions of the most prominently shifted bands of the non-specific and specific E-box probes are marked by single and double asterisks, respectively, on the right. ‘Probe’ at the bottom denotes the position of the free probe. (B) Gel mobility shift analysis was conducted as represented in (A) except that nuclear extracts prepared at the mesenchyme blastula stage were employed. (C) Gel mobility shift analysis was conducted as represented in (A) except that nuclear extracts prepared at the gastrula stage were employed. (D) Immunoshift analysis was performed. The wild-type OtxL probe was incubated with either nuclear extract (2 µg) alone prepared from embryos at the mesenchyme blastula stage (lane 1), or together with antiserum directed against recombinant HpUSF (lane 2) or with preimmune serum (lane 3).