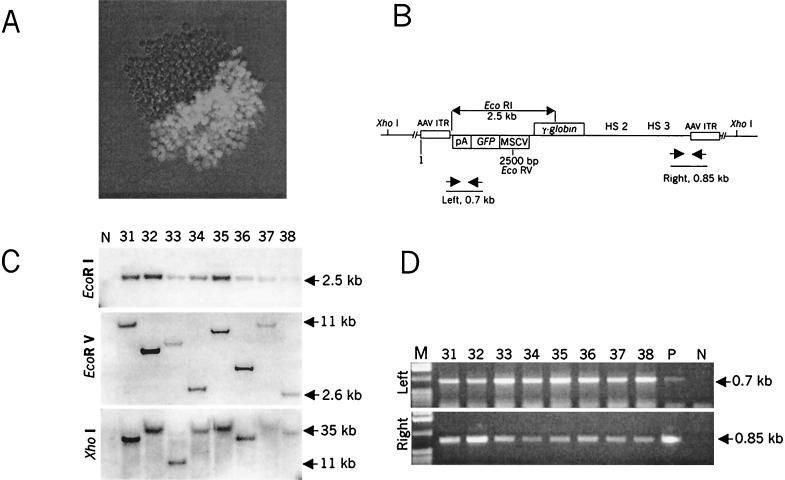
FIG. 3.
Analysis of GFP-positive clones transduced with ΔAd5/35.AAV. (A) GFP expression in a sample MO7e colony expanded for 14 days after infection with ΔAd5/35.AAV as described for Table 1. (B) Schematic representation of the localization of restriction sites and PCR primers in the integrated vector DNA. (C) Southern blot analysis of genomic DNA isolated from representative stable, GFP-positive, MO7e clones. Genomic DNA (10 μg) was digested with EcoRI, EcoRV, and XhoI with 2, 1, or 0 recognition sites, respectively, within the transgene cassette. Blots were hybridized with a GFP-specific probe. Note that at the time of analysis, clones contained different ratios of GFP-positive to GFP-negative cells (see Materials and Methods). N, negative control (DNA isolated from uninfected MO7e cells). (D) PCR analysis of the integrated transgene cassette. Genomic DNAs purified from representative GFP-expressing MO7e clones (1 μg) were subjected to PCR amplification to demonstrate the presence of intact left and right sequences of the vector in the same clone. Amplification was done as described in Materials and Methods.