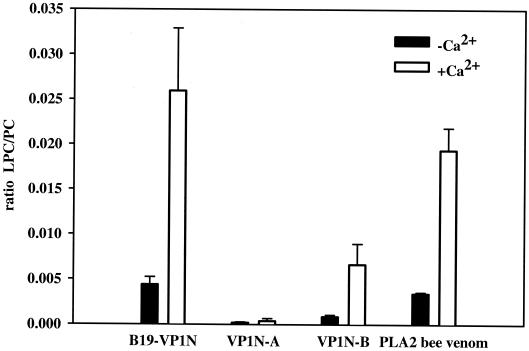
FIG. 2.
Phospholipase A2 assay. Comparison of the phospholipase A2 activities of the VP1 unique region (B19-VP1N) and shortened subfragments of the protein domain with that of a control bee venom phospholipase A2. The VP1 unique region (B19-VP1N), subfragments VP1N-A and VP1N-B (1 μM), and the bee venom phospholipase A2 (0.017 μM) were incubated at 37°C for 10 min with or without 10 mM calcium chloride. The basic reaction mixture was comprised of 100 μl of phospholipid liposomes containing 25 or 50 nM PC in 10 mM Tris buffer (pH 8.5). The reaction was stopped by the addition of methanol-chloroform (2:1 [vol/vol]). Lipids were extracted according to the method of Bligh and Dyer (3). The dried lipid extracts were dissolved in methanol-chloroform (3:1 [vol/vol]) containing 10 mM ammonium formate and characterized by electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. We used a Quattro LC triple-quadrupole mass spectrometer (Micromass, Manchester, United Kingdom) with the following settings: capillary, 3.5 kV; cone, 41 V; collision energy, 24 V; and collision gas pressure, 1.3 10−3 torr. Samples were injected at a constant flow rate of 75 μl/min with the Waters (Milford, Mass.) Alliance model 2790 filtration system and analyzed by a parent scan of m/z 184 specific for phosphocholine-containing lipids (6). The intensity of the ratio of hydrolyzed product (LPC) to substrate (PC) was used to determine the degree of phospholipase A2 activity. Standard deviations are indicated by bars.