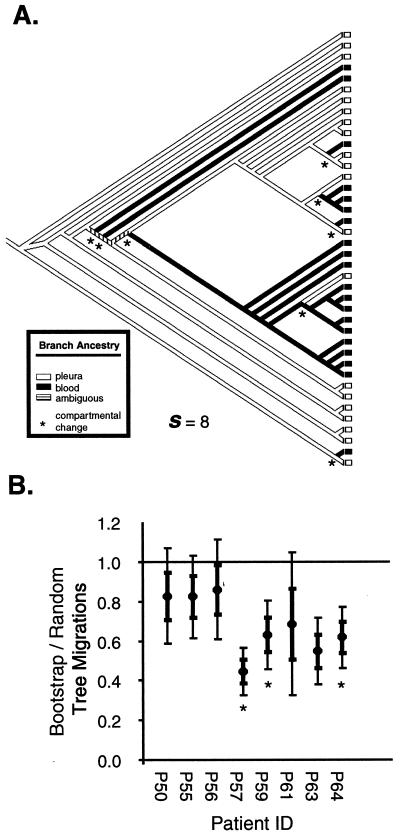
FIG. 4.
Phylogenetic and phenetic evaluation of blood and pleural compartmentalization in HIV-1-infected Ugandans with pleural TB. (A) Determination of compartmental changes. The source of each sequence is determined by the compartment from which it was isolated (blood or pleural space). The ancestry of each branch was determined by the sources of the terminal quasispecies so as to minimize compartmental changes, which occur when the ancestry of a branch changes. The sum total of compartmental changes (s) was calculated for each tree. (B) Migration events between compartments for the 1,000 actual bootstrap trees and 1,000 randomly constructed trees were constructed using the neighbor-joining method. Tree topology for the actual bootstrap trees was based on nucleotide sequence data for the C2-C3 region of the env (see Fig. 3 and Materials and Methods). Thin and thick error bars indicate 1 and 2 standard deviations of s ratios of actual to random trees, respectively. s ratios that fall 2 standard deviations below 1 are considered significant and suggest compartmentalization. Patients with significant blood and pleural compartmentalization of env quasispecies (P < 0.01) as determined by Mantel's test are marked by asterisks.