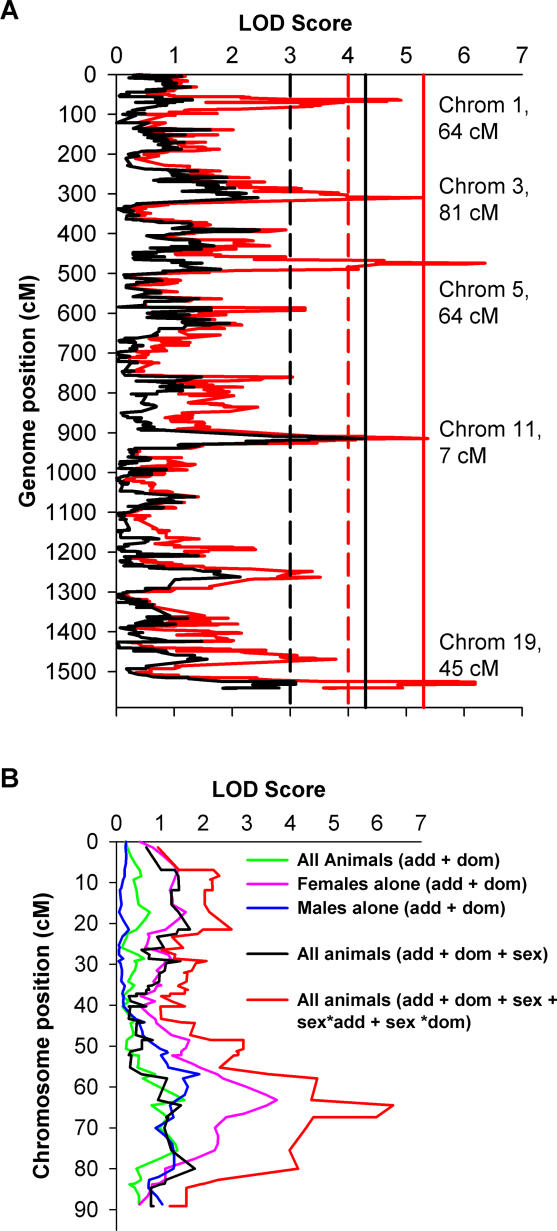
Figure 1. Genome Scan for Gonadal Fat Mass.
(A) Animals were genotyped at an average 1.5 cM density using 1,032 SNPs polymorphic between the parental strains. LOD scores computed using sex as an additive covariate (black) failed to detect significant linkage. A genome scan accounting for interactions between sex and QTL (red) showed evidence for suggestive linkage on Chromosome 1 and significant linkage on Chromosomes 3, 5, 11, and 19. Dashed and solid lines are thresholds for suggestive (p < 1 × 10−3) and significant linkage (p < 5 × 10−5), respectively.
(B) Genome scans for gonadal fat mass using different models over mouse Chromosome 5. Scans for fat mass using all animals with (black) and without (green) sex as an additive covariate failed to detect significant linkage. Females analyzed alone (magenta) showed evidence for suggestive linkage (p < 2 × 10−4). When both sexes were analyzed to account for sex effects (red), a significant QTL was realized (p < 10−6).
For clarity, only the model incorporating both the “sex*add” and “sex*dom” terms is shown in red, although additional models incorporating the terms separately were also computed.