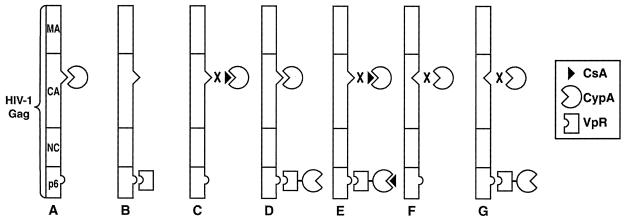
FIG. 1.
Model for in-trans CypA incorporation into HIV-1. (A) Under wild-type conditions, endogenous CypA is incorporated via the glycine 89-proline 90 CA region of HIV-1 Gag. (B) Vpr is incorporated via the p6 region of HIV-1 Gag. (C) CsA prevents endogenous CypA incorporation by competitively inhibiting CypA-Gag interactions. (D) In the absence of CsA, both endogenous CypA and CypA fused to Vpr are incorporated. (E) CsA prevents the incorporation of endogenous CypA but not that of the Vpr-CypA chimera. (F) Mutation of the glycine 89-proline 90 CA site inhibits endogenous CypA incorporation. (G) The Vpr-CypA chimera is incorporated despite the lesion in the glycine 89-proline 90 CA packaging signal.