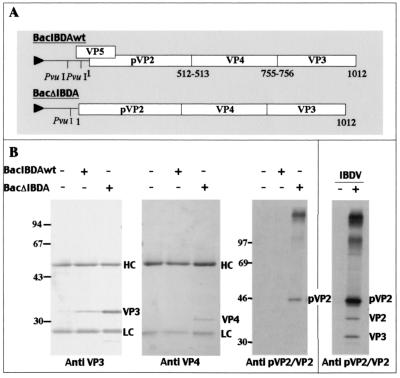
FIG. 1.
IBDA polyprotein-baculovirus recombinants. (A) Map of the two constructs derived from IBDA. In BacIBDAwt, the complete IBDA segment was placed under the control of the polyhedrin promoter, whereas in BacΔIBDA, part of the 5" end upstream of the polyprotein initiation codon was deleted. Numbers indicate the coordinates of P1-P"1 amino acids cleaved by the viral protease VP4, and the triangle upstream of the IBDA sequence indicates the polyhedrin promoter. (B) Immunoprecipitation analyses using an anti-VP3 antibody, an anti-VP4 antibody, and an anti-pVP2/VP2 antibody. Sf9 cells were infected by recombinant baculovirus, and LSCC-BK3 cells were infected by IBDV (right panel). +, infected cells; −, mock-infected cells. Immune complexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide) under reducing conditions. The gels were stained with Coomassie blue (left panels) or fluorographed for pVP2/VP2 immunoprecipitations (right panels). The relative Mrs (shown in thousands) were determined by reference to marker proteins. HC and LC indicate the positions of the heavy and light chains of the immunoglobulins, respectively. Note the presence of a VP3 band that coimmunoprecipitated with VP2 in BK3 cells infected by IBDV, an observation consistent with the presence of viral particles inside the cells.