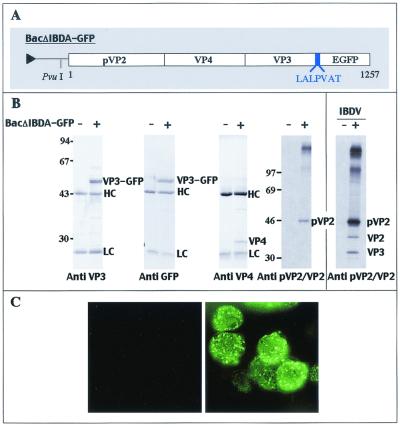
FIG. 4.
Expression of the fusion polyprotein IBDA-GFP in insect cells. (A) Schematic representation of the construct expressing the IBDA polyprotein fused at its C terminus with EGFP. A 7-aa linker was added between the two partners, and its sequence is reported using the single-letter code. (B) Expression of the fusion polyprotein IBDA-GFP in insect cells analyzed by immunoprecipitation with specific antibodies and by SDS-PAGE. Sf9 cells were infected with BacIBDA-GFP, and LSCC-BK3 cells were infected by IBDV (right panel). +, infected cells; −, mock-infected cells. Immune complexes were analyzed by SDS-PAGE (10% polyacrylamide) under reducing conditions. HC and LC indicate the positions of the heavy and light chains of the immunoglobulins, respectively. The gels were stained with Coomassie blue (left panels) or fluorographed for pVP2/VP2 immunoprecipitation (right panels). The relative Mrs (in thousands) were determined by reference to marker proteins, and positions of the molecular weight markers are indicated on the left. (C) Visualization of IBDA-GFP expression in Sf9-infected cells. The cells were examined under a optical microscope with UV light excitation 48 h postinfection. The left panel shows mock-infected cells, and the right panel shows infected cells.