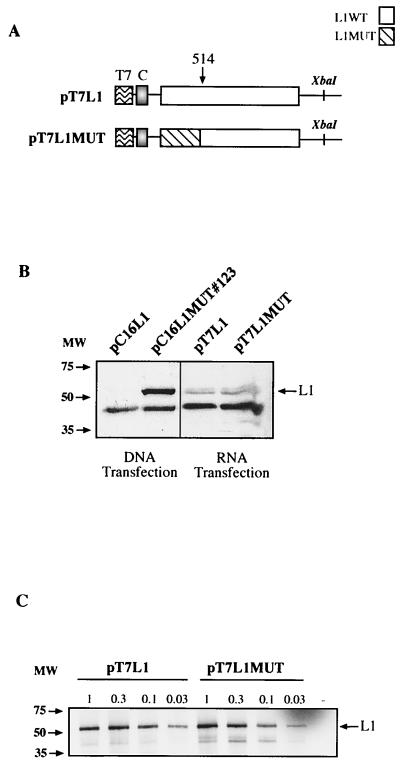
FIG. 10.
The inhibitory sequences in the HPV-16 L1 gene are not active in the cytoplasm. (A) Structures of the indicated expression plasmids. In plasmids pT7L1 and pT7L1MUT the CMV promoter is replaced by the T7 promoter, which was inserted immediately 5′ of position +1 in the CMV promoter, and the polyadenylation signal is flanked by the XbaI restriction site. XbaI-restricted plasmids were used for in vitro synthesis of capped mRNAs followed by in vitro polyadenylation. The sequences of these mRNA are therefore the same as the sequences of the mRNAs produced in the nuclei of cells transfected with corresponding eukaryotic expression plasmids pC16L1 and pC16L1MUT#123 (Fig. 5B), respectively. T7, bacteriophage T7 promoter; C, nucleotide +1 to +133 leader sequence from the CMV promoter. (B) Western blot analysis of extracts from cells transfected with pC16L1 or pC16L1MUT#123 plasmid DNA or capped and polyadenylated mRNAs produced in vitro from pT7L1 and pT7L1MUT. (C) In vitro translation of various amounts of pT7L1 or pT7L1MUT plasmid DNA in a coupled reticulocyte lysate in vitro translation system (Promega). The radiolabeled products were separated on sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis gels and then subjected to autoradiography. The HPV-16 L1 protein is indicated.