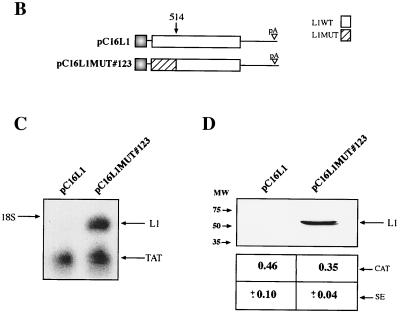
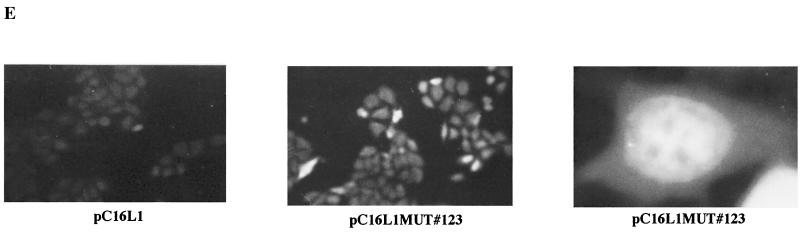
FIG. 5.
Mutational analysis of the inhibitory sequences in the HPV-16 L1 coding sequence. (A) The sequences of the wild-type (WT) and mutant (MUT) HPV-16 L1 gene sequences from position 1 to 514 is shown. Numbering starts at the first purine in the translational start codon of the L1 gene coding sequence. Altered nucleotides are in boldface italics. The StyI, MscI, and BamHI sites at nucleotides 188, 356, and 514, respectively, are indicated. Arrowhead, nucleotide 129. (B) Structures of the plasmids expressing the wild-type and the mutant HPV-16 L1 genes. (C) Northern blot of total cytoplasmic RNA harvested from HeLa cells transfected with the two plasmids shown in panel B. Plasmid pCTAT (42), expressing the HIV-1 tat cDNA (33), was included as an internal control for transfection efficiency. (D) Western blot of extracts from HeLa cells transfected with the two plasmids shown in panel B. The L1 protein is indicated. The CAT protein levels produced from internal control plasmid pCCAT and standard errors from triplicate experiments are shown. (E) Indirect immunofluorescence on HeLa cells transfected with the two plasmids shown in panel B. The cells were stained with an anti-HPV-16 L1 peptide antiserum (13).