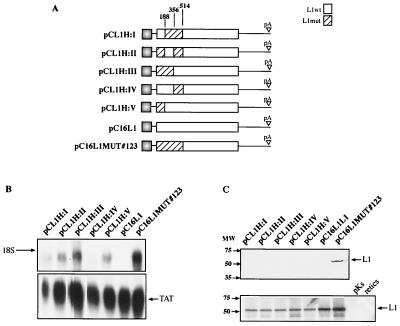
FIG. 6.
Mapping of inhibitory sequences in the HPV-16 L1 gene using hybrids between wild-type (wt) and mutant (mut) HPV-16 L1 gene sequences. (A) Structures of the plasmids expressing the wt and the mutant HPV-16 L1 genes. Numbering starts at the first purine in the translational start codon of the L1 coding sequence. The StyI, MscI, and BamHI sites at nucleotides 188, 356, and 514, respectively, which were used to generate the hybrids, are indicated. pA, poly(A). (B) Northern blot of total cytoplasmic RNA harvested from HeLa cells transfected with the plasmids shown in panel A. Plasmid pCTAT (42), expressing the HIV-1 tat cDNA (33), was included as an internal control for transfection efficiency. (C) (Top) Western blot of extracts from HeLa cells transfected with the plasmids shown in panel A. The filter was incubated with an anti-HPV-16 L1 peptide antiserum (13). (Bottom) In vitro translation of the various L1 coding sequences in the plasmids shown in panel A after insertion downstream of the T7 promoter in pBluescript. The radiolabeled products were analyzed by autoradiography. pKS, in vitro translation of empty pBluescript vector; retics, in vitro translation reaction in the absence of plasmid DNA.