Full text
PDF









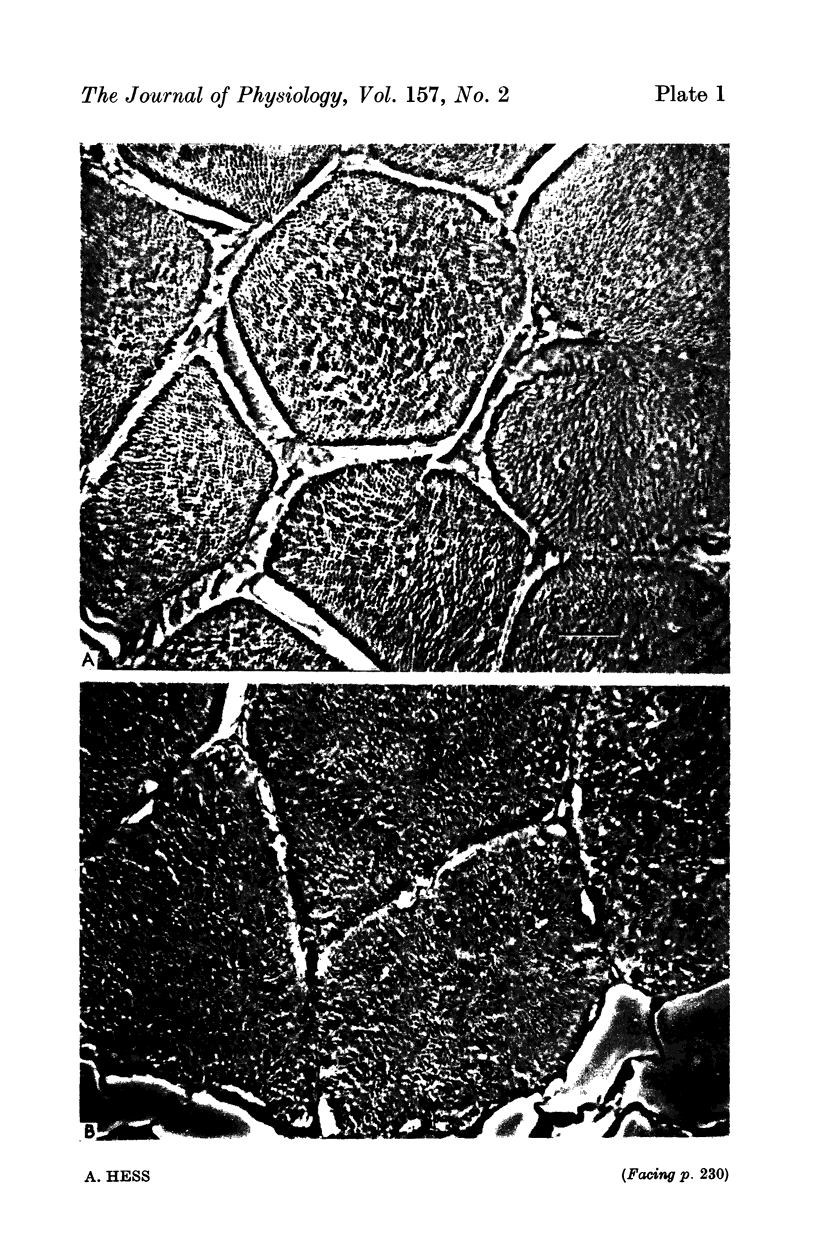




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BARETS A. Caractéristiques morphologiques des deux types d'innervation motrice du muscle latéral des Téléostéens. C R Seances Soc Biol Fil. 1955 Jul;149(13-14):1420–1422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARETS A., FESSARD A., LE TOUZE S. Etude électrophysiologique d'un type particulier de jonction neuromusculaire: le système moteur rapide des Téléostéens. J Physiol (Paris) 1956 May-Jun;48(3):381–383. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BARETS A., LE TOUZE S. Identification dans le muscle latéral d'un téléostéen, Tinca tinca L. de deux systèmes moteurs, lent et rapide. C R Hebd Seances Acad Sci. 1956 Feb 27;242(9):1230–1233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BISHOP G. H. Natural history of the nerve impulse. Physiol Rev. 1956 Jul;36(3):376–399. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1956.36.3.376. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DIETE-SPIFF K., PASCOE J. E. The spindle motor nerves to the gastrocnemius muscle of the rabbit. J Physiol. 1959 Dec;149:120–134. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006329. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EYZAGUIRRE C. The electrical activity of mammalian intrafusal fibres. J Physiol. 1960 Jan;150:169–185. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006380. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GINSBORG B. L. Spontaneous activity in muscle fibres of the chick. J Physiol. 1960 Mar;150:707–717. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006413. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G. The spindle and extrafusal innervation of a frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):416–430. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G. The structures of fast and slow muscle fibres in the frog. J Anat. 1958 Oct;92(4):559–562. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A. The structure of extrafusal muscle fibers in the frog and their innervation studied by the cholinesterase technique. Am J Anat. 1960 Sep;107:129–151. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001070204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A. Two kinds of motor nerve endings on mammalian intrafusal muscle fibers revealed by the cholinesterase technique. Anat Rec. 1961 Feb;139:173–183. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091390209. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KATZ B. The efferent regulation of the muscle spindle in the frog. J Exp Biol. 1949 Aug;26(2):201–217. doi: 10.1242/jeb.26.2.201. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K., NISHI S. Action potentials of single intrafusal muscle fibres of frogs. J Physiol. 1957 Jul 11;137(2):193–209. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005806. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KOKETSU K., NISHI S. An analysis of junctional potentials of intrafusal muscle fibres in frogs. J Physiol. 1957 Nov 14;139(1):15–26. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1957.sp005871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUEGER P. [Innervation of phasic or tonic reacting muscles of mammals and humans]. Acta Anat (Basel) 1960;40:186–210. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUGER P., GUNTHER P. G. Fasern mit "Fibrillenstruktur" und Fasern mit "Felderstruktur" in der quergestreiften Skeletmuskulatur der Säuger und des Menschen; eine Entgegnung. Z Anat Entwicklungsgesch. 1955;118(4):312–323. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRUGER P., GUNTHER P. G. Innervation und pharmakologisches Verhalten des M. gastrocnemius und M. pectoralis maior der Vogel. Acta Anat (Basel) 1958;33(4):325–338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., HUNT C. C. The mammalian small-nerve fibers: a system for efferent nervous regulation of muscle spindle discharge. Res Publ Assoc Res Nerv Ment Dis. 1952;30:24–47. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Properties of the 'slow' skeletal muscles fibres of the frog. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):318–340. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004949. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Small-nerve junctional potentials; the distribution of small motor nerves to frog skeletal muscle, and the membrane characteristics of the fibres they innervate. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):289–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MACKAY B., MUIR A. R., PETERS A. Observations on the terminal innervation of segmental muscle fibres in amphibia. Acta Anat (Basel) 1960;40:1–12. doi: 10.1159/000141568. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TAKEUCHI A. Neuromuscular transmission of fish skeletal muscles investigated with intracellular microelectrode. J Cell Comp Physiol. 1959 Dec;54:211–220. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1030540302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TIEGS O. W. Innervation of voluntary muscle. Physiol Rev. 1953 Jan;33(1):90–144. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1953.33.1.90. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]