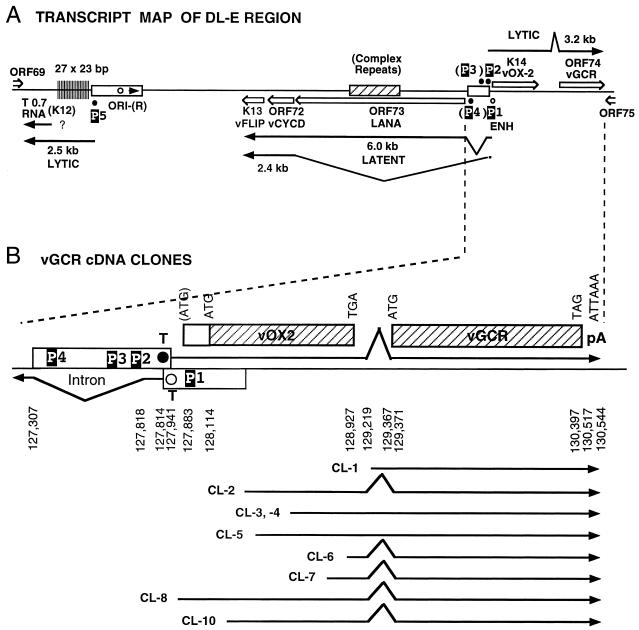
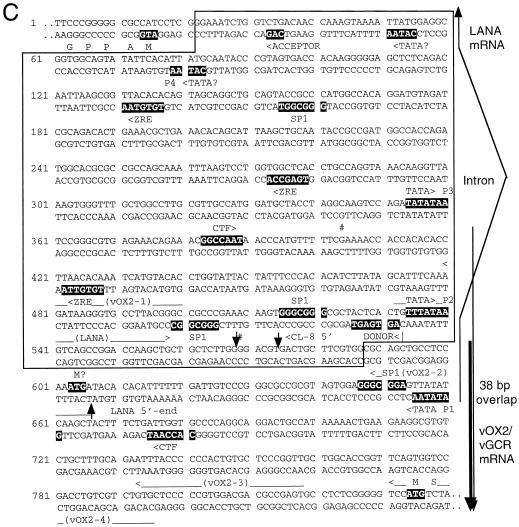
FIG. 2.
Genomic organization of the DL-E region of KSHV, including the T0.7/K12, vFLIP, vCYCD, LANA1, vOX2, and vGCR genes and their upstream control elements. (A) Structural map of the 13-kb DL-E region, showing sizes and orientations of all known mRNA species and the positions of five known or potential promoters (P1 to P5). (B) Summary map of the nine cloned vGCR cDNAs analyzed, illustrating relative positions of the 5′ termini, their 3′-coterminal features, and the presences or absence of the 147-bp intron between the vOX2 (K14) and vGCR (ORF74) coding regions. (C) Sequence organization of the divergent LANA1 and vOX2/vGCR promoter control regions. The entire 840-bp sequence shown represents genomic nucleotide coordinate positions 127281 to 128120 (58). The divergent 505-bp promoter region contained in the vOX2(F)-LUC and vOX2(R)-LUC reporter genes is boxed. The relative directions and overlap between the 5′ ends of the latent LANA1 mRNA and the lytic cycle vOX2/vGCR mRNA are indicated on the right. Consensus likely transcriptional control motifs such TATA, SP1, and CTF binding sites, potential ZTA binding motifs (ZRE), and LANA1 splice donor and acceptor signals are all denoted in reversed-out type. Solid vertical arrowheads indicate the 5′ ends of LANA1 (position 127887) and vOX2/vGCR (position 127849) mRNA determined here by primer extension analysis, and the open vertical arrowhead indicates the 5′ end (position 127854) of the longest vOX2/vGCR cDNA clone obtained (cl-8). # symbols indicate the two 5′ start sites at positions 127685 and 127849 detected by the 5′RACE technique with uninduced mRNA. Named oligonucleotide primers (LANA1, vOX2-1, vOX2-2, vOX2-3, and vOX2-4) used for RNA extension and 5′RACE analysis are denoted by horizontal arrows underneath the corresponding sequences.