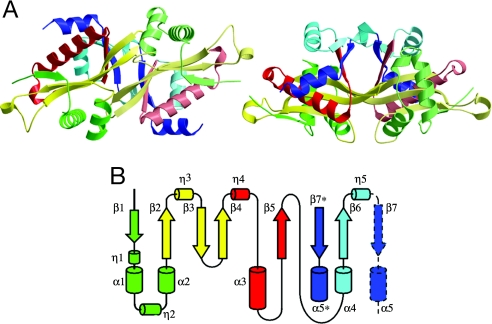
Fig. 1.
Structure of apoSSAT. (A) Ribbon diagram showing two orthogonal views of the asymmetric dimer colored according to the topology diagram in B. (B) Topology of the secondary structure elements in chain A. From the N terminus, secondary structure elements are colored green (β1, η1, α1, η2, and α2), yellow (β2, η3, β3, and β4), red (η4, α3, and β5), cyan (α4, β6, and η5), and deep blue (β7 and α5). The C-terminal elements β7 and α5 (enclosed in a broken black line) form part of the core structure of the opposing monomer. The structure represented is that of PDB ID 2B5G5, in which density was not observed for residues 28–31 and 170–171 of chain A nor for residues 2–3, 47–50, 61–63, or 171 of chain B.