Figure 3.
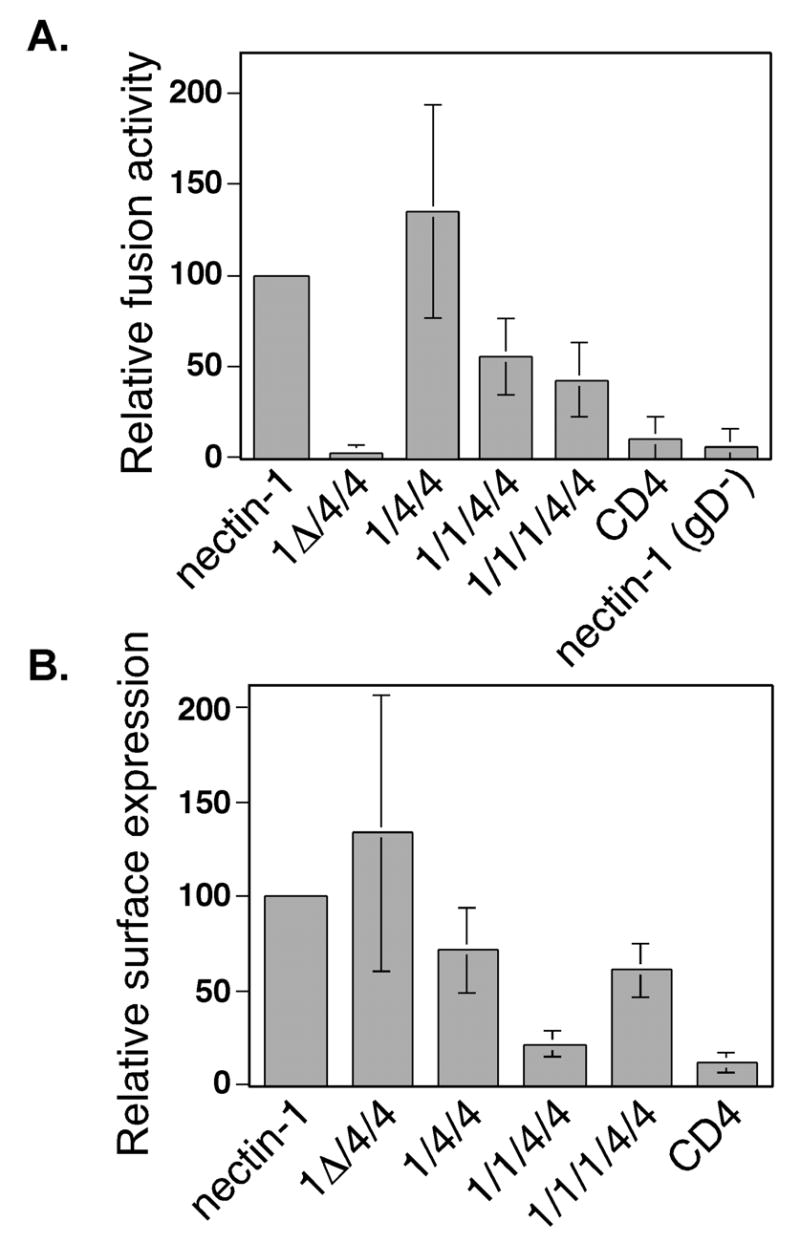
Fusion activity of nectin-1α/CD4 chimeras in a cell-mixing fusion assay. (A) Fusion assay. CHO-K1 cells expressing gB, gD, gH, gL, and T7 polymerase, or control plasmid pCAGGS instead of gD plasmid (gD−), or all control plasmid pCAGGS (control) were mixed with CHO-K1 cells expressing nectin-1α or chimera and pG1NT7β-gal. Within each experiment, all values were expressed as a percentage of the value obtained for the positive control (nectin-1). (B). Cell-surface expression of chimeras in the fusion assay. CELISA analysis of cells from (A) using the nectin-1 mAb CK6. Within each experiment, all values were expressed as a percentage of the value obtained for the positive control (nectin-1). The 1Δ/4/4 chimera, however, was not efficiently recognized by CK6 so another anti-nectin-1 V-like domain mAb, CK5, was used and the resulting values were expressed as a percentage of the results obtained for nectin-1-expressing cells with CK5. The fusion/CELISA experiments were performed three times and the mean values plus standard deviations for the combined relative results are depicted.
