Fig. 1.
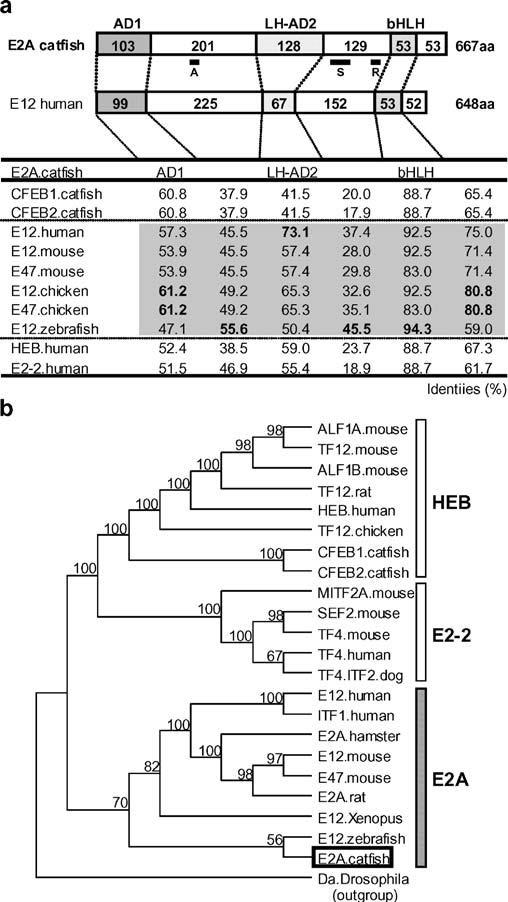
The structure and evolutionary relationships of catfish E2A. a Schematic depiction of the domain structure of catfish E2A in comparison with human E12, shown above a table of percent identities. The lengths (amino acid sequence) of the activation domain 1 (AD1), the loop-helix activation domain 2 (LH-AD2), the basic helix–loop–helix (bHLH) domain, and the intervening regions are shown. The table lists the percent identities of the inferred amino acid sequences of the domains (AD1, LH-AD2, bHLH, and their intervening regions) of the catfish E2A as compared with those published for other species. Top, A, S, and R indicate the position of the peptide sequence used for antibody production, the probe sequence used in the S1 nuclease protection assay, and the Rep domain, respectively. b Phylogenetic tree of vertebrate E-proteins. The class I bHLH daughterless protein (Da) of Drosophila was used as the outgroup. Catfish E2A, is indicated by an open box, and bootstrap values (>50%) in support of each node are shown
