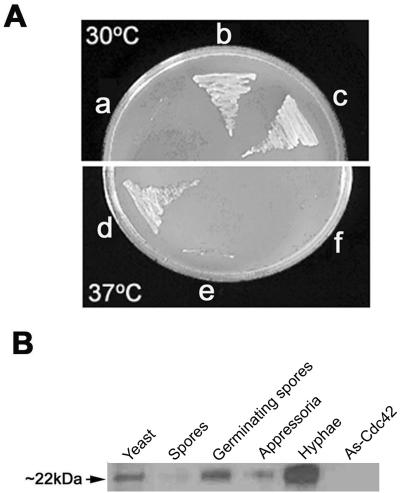
FIG. 1.
CtCdc42 restores the wild-type phenotype to a yeast mutant. (A) Complementation of the temperature-sensitive phenotype of S. cerevisiae DJTD2-16A (Cdc42 disruptant) with CtCdc42. The pYES2 vector or pYES2-CtCdc42 plasmid was transformed into S. cerevisiae DJTD2-16A. Each clone was streaked on an SD Gal plate lacking Ura and subsequently incubated at 30°C or 37°C for 3 days. a and f, recipient strains; b and e, cells transformed with the empty vector pYES2; c and d, cells transformed with pYES2-CtCdc42. (B) Developmental Western blot analysis of CtCdc42. Total protein (20 μg per lane) was isolated from spores, germinating spores, appressoria, and vegetatively growing hyphae, as described in Materials and Methods. Protein extracts from yeast strain EGY48 and the antisense Cdc42 (As-Cdc42) mutant were used as positive and negative controls, respectively. A yeast-derived Cdc42p antibody (Santa Cruz Biotechnology) was used to detect the expression levels of the CtCdc42 protein in different developmental stages.