Fig. 5.
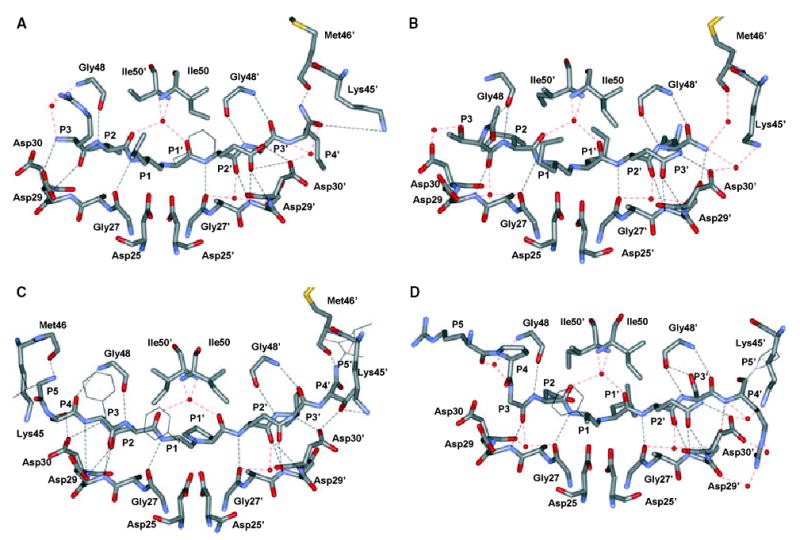
Hydrogen bond interactions between protein and inhibitor. Hydrogen bond interactions are shown for interatomic distances of 2.5– 3.3 Å. Water molecules are indicated by red spheres. Water-mediated hydrogen bonds are shown as red dashed lines, while direct interactions between the protease and inhibitor are in black. (A) Hydrogen bond interactions between HIV-1 protease with the V82A mutation (PRV82A) and CA-p2. (One water-mediated interaction between P3 Arg and Pro 81′ is not shown.) (B) Hydrogen bond interactions between PR and p2-NC. (Water-mediated interactions of both termini of inhibitor with Arg8 and 8′ are not shown.) (C) Hydrogen bond interactions between PR and p6pol-PR. (Water-mediated interactions of the C termini of p6pol-PR with Asp60 and Gln61 are not shown.) (D) Hydrogen bond interactions between PRV82A and p1-p6. (Water-mediated interactions of the C termini of p1-p6 with Trp6, Arg8 and Arg87′ are not shown.)
