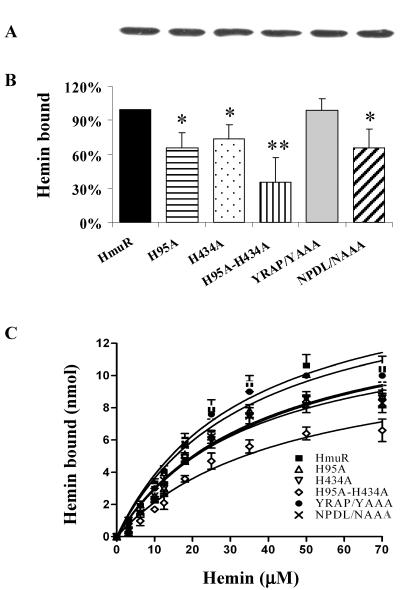
FIG. 6.
Binding of hemin (B and C) to E. coli cells expressing wild-type HmuR and HmuR with site-directed mutations. The level of rHmuR expression (A) was determined by SDS-PAGE and Western blot analysis of outer membrane fractions as described in Materials and Methods. The binding of hemin (10 μM hemin in B) to whole E. coli cells was determined by a decrease of absorbance of the supernatant of the samples compared to the control sample containing only hemin. Binding to E. coli cells expressing HmuR site-directed mutants was then compared with that to E. coli cells expressing wild-type HmuR, which was set arbitrarily at 100%. Five independent experiments were performed in triplicate. Data are means ± standard deviation. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01 for E. coli expressing HmuR with point mutations versus E. coli harboring wild-type HmuR. Binding of hemin as a function of concentration (C) was determined as described previously (41).