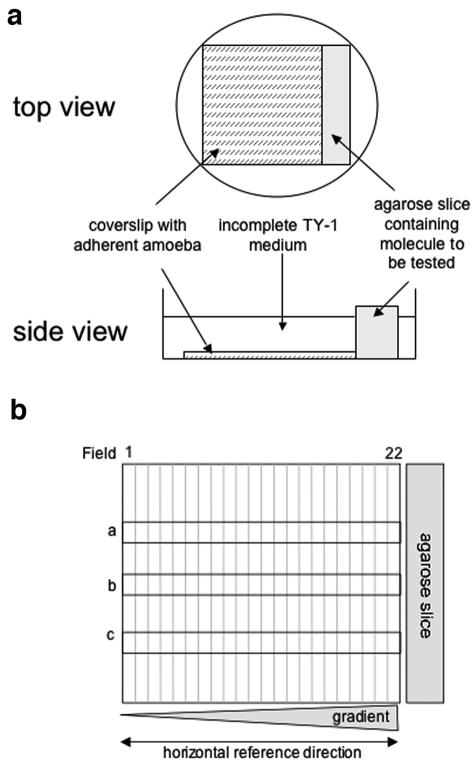
FIG. 1.
“Chemotaxis-on-coverslip assay” setup. (a) Experimental setup. One milliliter of incomplete TY-1 medium, without decomplemented serum, vitamins, or penicillin-streptomycin (iTY-1), containing 2.5 × 105 E. histolytica trophozoites previously treated with fluorescent CellTracker green (Molecular Probes) was deposited onto a coverslip placed in a 35-mm culture dish. The trophozoites were allowed to adhere for 10 min at 37°C, during which time the test molecules were injected into a slice of 1% agarose (20 mm by 5 mm by 5 mm). The excess medium was removed from the dishes, the agarose slice was placed next to the coverslip, and 1.5 ml of iTY-1 was then added to the dish. E. histolytica is an anaerobic organism, so the level of oxygen was minimized by placing the dishes in an anaerobic environment (GENbag anaer; Biomerieux). The cells were incubated at 37°C for 2 hours. The trophozoites were fixed with 3.7% paraformaldehyde for 20 min at room temperature. The coverslips were mounted onto glass slides so that the cell distribution could be examined. The progression of Ponceau red (5 μl of a 3.75% solution injected into the agarose slice) was monitored as a measure of the stability of the gradient. A stable, linear gradient was found at between 1 and 3 h. (b) To quantify the cell distribution, the trophozoites were imaged with a Zeiss inverted microscope in epifluorescence mode (fluorescein filters), running the “mosaic” option of the Simple PCI software. The coverslip's vertical axis was divided into 22 fields, with field 22 nearest the agarose slice. Three horizontal rows (a, b, and c) of 22 adjacent images were taken along the coverslip (covering 10% of the coverslip's area). The number of trophozoites was counted in each field for rows a, b, and c, so as to obtain the total number of amebae per field. The total population counted was obtained by summing the number of parasites in rows a, b, and c for the 22 fields.