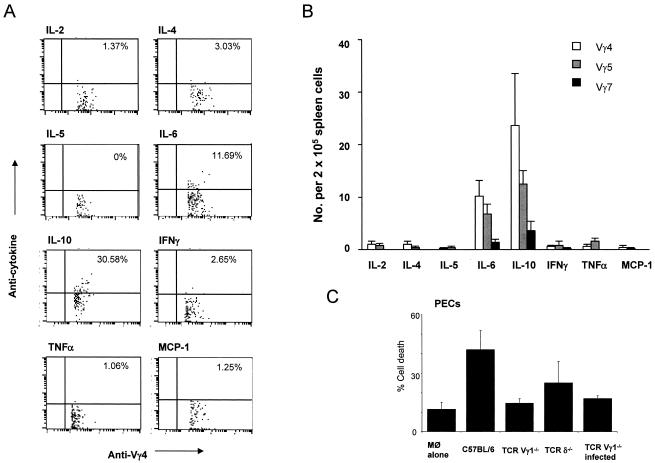
FIG. 5.
Functional properties of γδ T cells responding to Listeria infection in Vγ1−/− mice. Cytokine synthesis by Vγ4+, Vγ5+, and Vγ7+ T cells elicited in response to Listeria infection was determined by staining splenocytes with TCRγδ-, CD3-, and TCR-Vγ-specific antibodies in conjunction with anticytokine antibodies and flow cytometric analysis as described in Materials and Methods. Representative dot plots are shown (A), with percentages of Vγ4 T cells positive for each marker indicated, and results for Vγ4, Vγ5, and Vγ7 subsets were compiled from three independent experiments (B). The ability of splenocytes from Listeria-infected Vγ1−/− mice (TCR-Vγ1−/− infected) enriched for Vγ4+, Vγ5+, Vγ6+, and Vγ7+ T cells to kill target peritoneal macrophage obtained from day 8 Listeria-infected TCRδ−/− mice was determined using a fluorescent-based cytotoxicity assay as described in Materials and Methods (C). As controls, target PECs were cultured alone (Mφ alone), and splenocytes from noninfected wild-type (C57BL/6), Vγ1−/−, or TCRδ−/− mice were used as additional sources of effector cells. IFNγ, gamma interferon; TNFα, tumor necrosis factor alpha; MCP-1, monocyte chemoattractant protein 1; No., number.