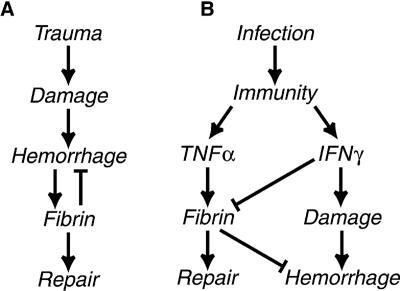
FIG. 7.
Models depicting the disparate mechanisms that regulate fibrin deposition during trauma and infection. (A) The conventional trauma-activated hemostatic coagulation pathway. (B) Our proposed model of cytokine-regulated coagulation during infection: TNF-α promotes fibrin deposition while IFN-γ suppresses fibrin deposition and also promotes hemorrhage. Note that fibrin deposits in response to damage in the conventional hemostatic pathway, whereas fibrin can be deposited preemptively, thereby limiting hemorrhage and hastening tissue repair in the cytokine-regulated pathway.