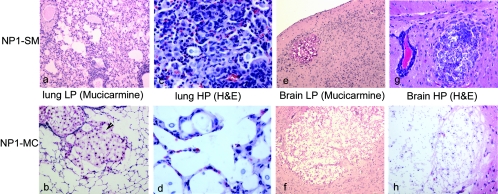
FIG. 3.
Inflammatory responses in NP1-SM- and NP1-MC-infected mice. An extensive inflammatory response was detected in the lungs of NP1-SM (i.t.)-infected mice (a), whereas NP1-MC (i.t.)-infected mice exhibited a minimal inflammatory response and developed large cryptococcomas (b). A high magnification (HP) (×400) demonstrated more infiltration of mononuclear cells in the lung tissue of NP1-SM (c)- than of NP1-MC (d)-infected mice. In contrast, both NP1-SM- and NP1-MC-infected (i.v.) mice exhibited cryptococcomas (e and f) in the brain, although the cryptococcomas in the NP1-SM (e)-injected mice were smaller. Upon higher magnification (×200), it also appeared that NP1-SM elicited more inflammation in the brain (g) compared to the cryptococcomas in NP1-MC-infected mice (f and h). H&E, hematoxylin and eosin.