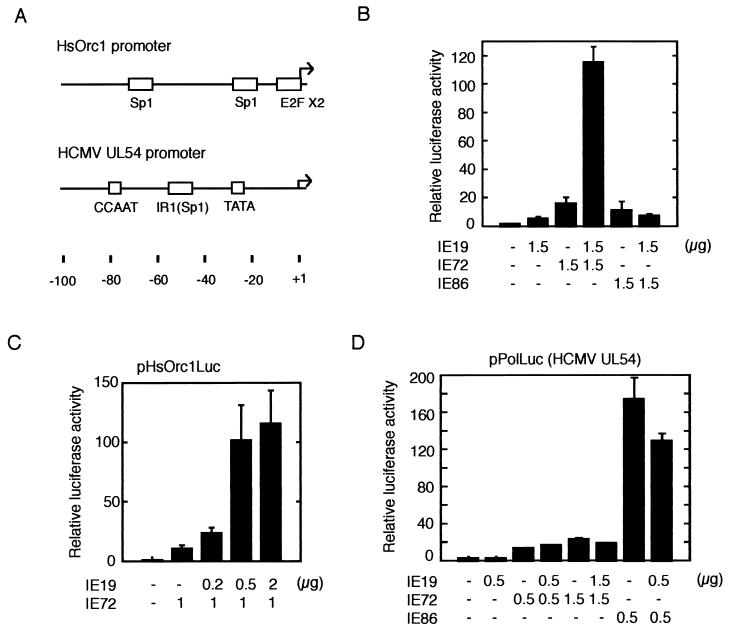
FIG. 7.
Activation of HsOrc1 promoter by IE19 and IE72. (A) Promoter regions of the HsOrc1 and UL54 genes are shown. Arrows indicate the transcription initiation sites. For the HsOrc1 gene, only a major initiation site is shown here. Sp1, E2F, CCAAT, and TATA elements are indicated by open boxes. Nucleotide numbers relative to the initiation site are indicated. (B) Activation of the HsOrc1 promoter by IE19, IE72, and/or IE86 was examined using the HsOrc1 luciferase reporter plasmid (pHsOrc1Luc), which contains the HsOrc1 promoter region from −1053 to +182. The expression plasmid for IE72, IE86, and/or IE19 (1.5 μg each) was transfected into the human glioblastoma cell line U373MG with pHsOrc1Luc (1 μg) and an internal control plasmid, pRSVLacZ (1 μg). The total amount of transfected plasmids was adjusted with an additional control plasmid. Cells were harvested 2 days after transfection, and the luciferase and β-galactosidase activities were measured. The luciferase activity was normalized to the β-galactosidase activity in the same extract and shown as activity relative to that for the vector plasmid-transfected sample. Three experiments were performed to obtain the average activity with standard error. (C) Activation of the HsOrc1 promoter was dose dependent on the IE19 expression plasmid. Various amounts of pME-IE19 (0, 0.2, 0.5, and 2 μg) were cotransfected with a fixed amount of pME-IE72 (1 μg) in an HsOrc1 reporter assay. Results are shown as for panel B. (D) Activation of the UL54 promoter was examined using the UL54 luciferase reporter plasmid. Expression plasmid(s) (pME-IE72, pME-IE86, and/or pME-IE19) was transfected with pPolLuc (1 μg) in a similar reporter assay. Results are shown as for panel B.