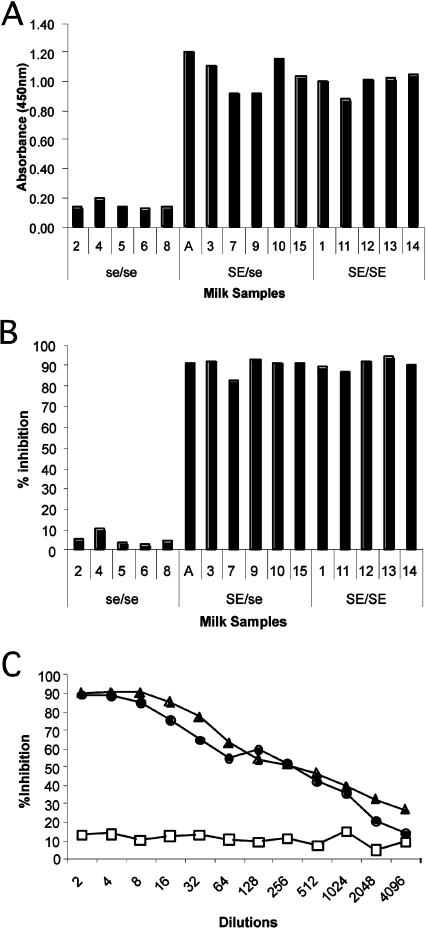
Figure 1. FUT2-dependent molecules from human milk inhibit rNV VLP attachment to H type 1 histo-blood-group antigen.
(A) Milk samples from women genotyped for the FUT2 locus were coated on to ELISA plates at a dilution of 1:1000 and the presence of H type 1-reactive molecules was determined by reactivity of the anti-H type 1/Leb mAb, LM137. A total of five women were considered as non-secretors (2, 4, 5, 6 and 8) and the remaining as secretors. SE=active FUT2 alelle; se=inactive FUT2 allele. (B) Inhibition of rNV VLP attachment to polyacrylamide-conjugated H type 1 by milk samples from secretor and non-secretor women diluted to 1:10. (C) Examples of the inhibitory potency of milk samples, from 2 secretors (●, ▲) and a non-secretor (□), on rNV VLP attachment to saliva from an O type secretor individual. The inhibition assay was performed as described in the Materials and methods section. The percentage of inhibition is shown as a function of the reciprocal milk dilution.