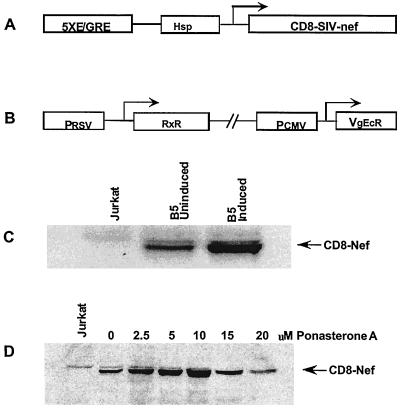
FIG. 1.
Inducible stable expression of CD8-Nef in Jurkat cells. (A) Schematic diagram of the pIND-CD8-Nef construct. The coding sequence for the CD8-Nef chimera was cloned into the pIND vector downstream of the coding sequence for the hybrid E/GRE and minimal Hsp promoters. (B) Schematic diagram of the pVgRxR regulatory plasmid. This plasmid encodes Drosopila ecdysone hormone receptor subunits RxR and EcR under the control of Rous sarcoma virus (RSV) and cytomegalovirus (CMV) promoters, respectively. (C) Generation of the B5 stable cell line. Jurkat cells were stably transfected with pIND-CD8-Nef and pVgRxR plasmids. Clones resistant to both G-418 and Zeocin were screened for Nef expression by immunoblotting using an anti-Nef antibody. Clone B5 was selected and showed a fivefold increase in Nef expression following induction. There was a basal level of Nef expression in the absence of ponasterone A. (D) Induction of CD8-Nef expression is dependent on ponasterone A concentrations. B5 cells were treated with increasing concentrations of ponasterone A. Cell lysates containing equal amounts of proteins were immunoblotted with an anti-Nef antibody. Nef expression peaked at 10 μM ponasterone A but declined at 15 and 20 μM ponasterone A.