Fig. 1.
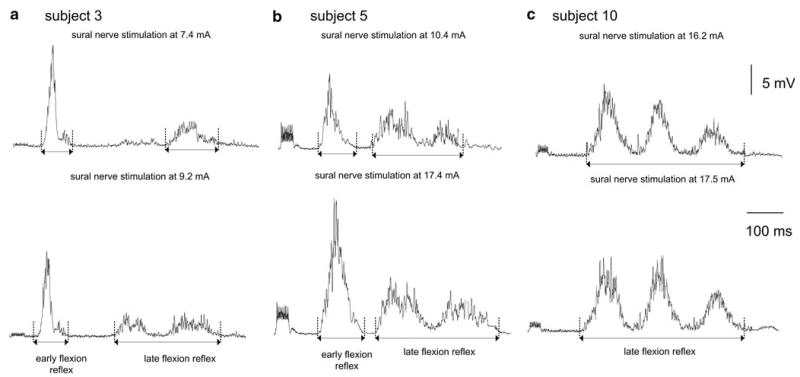
The full-wave rectified EMG averages of the two classes of the flexion reflex are identified by vertical cursors placed at the start and at the end of the corresponding EMG burst. For all three subjects, the top EMG corresponds to the stimulation intensity during which a response in the tibialis anterior muscle was first observed. In subject 10 (c), the early flexion reflex was absent when the sural nerve was stimulated at non-nociceptive stimulus intensities
