Fig. 7.
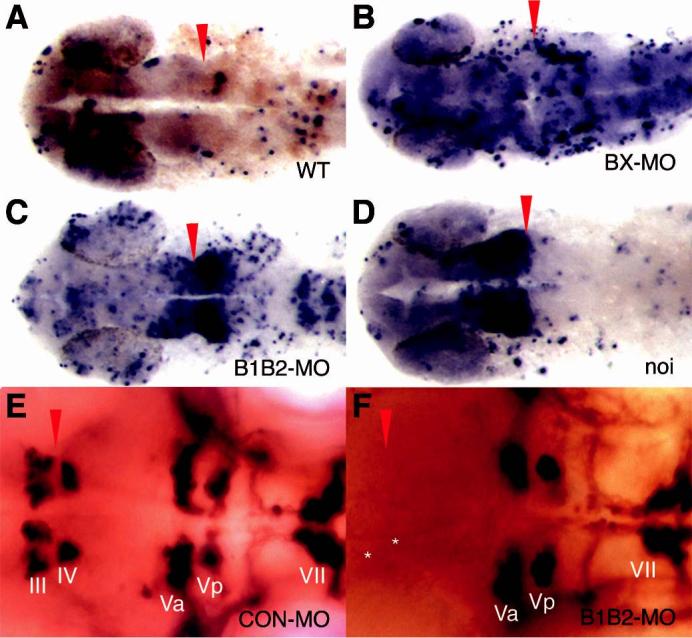
Knockdown of Lmx1b.1 and Lmx1b.2 results in increased cell death around the IsO, with a concomitant failure of neural differentiation. (A-D) A TUNEL assay stains apoptotic cells blue. Dorsal views with anterior left. (A) A low level of randomly distributed apoptosis is detected in wild type embryos. (B) Injection of BX-MO results in a nonspecific increase in apoptosis. (C) Injection of B1B2-MO sharply increases apoptosis in the IsO, especially caudally. Nonspecific apoptosis is also increased. (D) Increased apoptosis is detected around the IsO in embryos homozygous for the pax2.1/no isthmus mutation, especially rostrally. (E, F) Cranial motor neurons were visualised by expressing GFP under the control of the Islet-1 promoter and staining with an antibody against GFP. (E) Cranial motor neurons III and IV flank the IsO. (F) Neurons III and IV fail to form in B1B2-MO-injected embryos, while other neurons are unaffected. Red arrowheads indicate position of the MMR and asterisk mark normal position of missing neurons.
