FIG. 3.
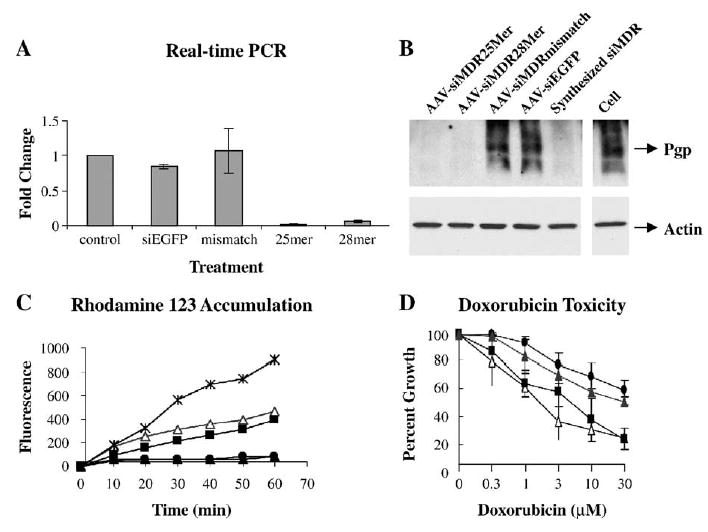
Inhibition of MDR1 and reversal of the drug-resistant phenotype by scAAV-delivered hairpin siRNA in NCI/ADR-RES cells. (A) Real-time RT-PCR analysis of MDR1 mRNA level. MDR1 mRNAs from the cells treated with scAAV (1200 particles/cell, or 5000 particles/cell for 28-mer) were quantified by real-time PCR. Values were normalized to those of GAPDH and expressed as fold change over untreated cells. Each experiment was repeated three times and means and standard errors are shown. (B) Western blot of P-glycoprotein. The scAAV treatments were as in A; in addition one set of cells was treated with the chemically synthesized anti-MDR1 siRNA described in Table 1 (200 nM, using Lipofectamine 2000). Top: P-glycoprotein was detected with C219 antibody. Bottom: The same membrane was reprobed with anti-actin antibody. (C) Rhodamine 123 uptake. Cells infected with scAAV producing 25-mer (open triangles), 28-mer (solid squares), or mismatch (solid triangles) hairpin MDR1 siRNA or untreated cells (solid circles) were exposed to 1 μg/ml Rh123 for various times. A comparison is shown to non-drug-resistant MCF7 breast carcinoma cells (X marks). Repeat experiments gave similar results. (D) The cytotoxicity profile of Adriamycin. Cells infected with scAAV (1200 particles/cell, or 5000 particles/cell for 28-mer) producing 25-mer (open triangles), 28-mer (solid squares), or mismatch (solid triangles) hairpin MDR1 siRNA or untreated cells (solid circles) were exposed for 24 h to various concentrations of Adriamycin (doxorubicin). After a further 48 h in complete growth medium, cell numbers were determined and expressed as percentage of control.
