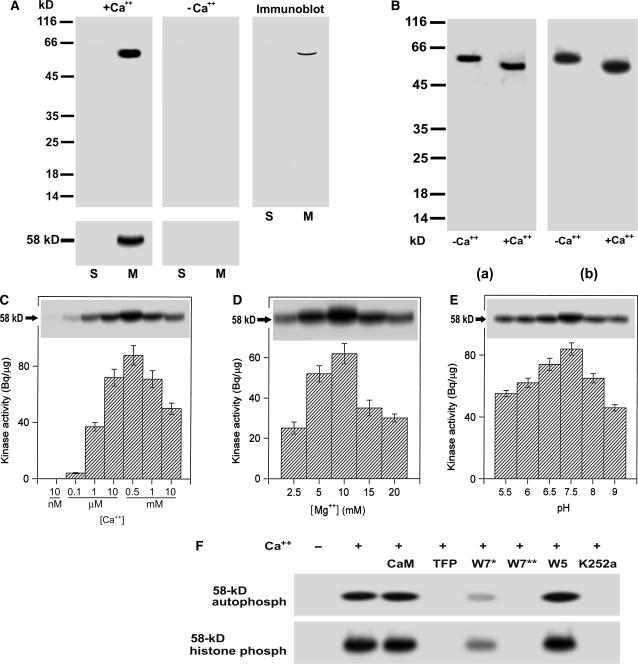
Figure 1.
Biochemical characterization of a 58-kD membrane-associated Ca+-dependent protein kinase in grape berry. A, A 58-kD membrane-associated Ca2+-dependent protein kinase is present in grape berry. Soluble fraction (lanes labeled S, 40 μg of protein) and microsomes (lanes labeled M, 20 μg of protein) were separated on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel. The separating gel for assaying kinase catalytic activity was polymerized in the presence of histone III-S. Autophosphorylation and kinase activities were assayed in the presence (+Ca2+) or absence (−Ca2+) of free Ca2+ as described in “Materials and Methods.” The molecular masses of protein standards are shown at the left of the sections in kD. Autophosphorylating (gels above) and histone-phosphorylating activity (gels below) of 58-kD kinase are shown in the left and middle sections, and immunoblotting in the right section. Immunoblotting was done with the antiserum directed against the CaM-like domain of soybean CDPKα as described in “Materials and Methods.” B, Ca2+-dependent electrophoretic mobility shift of the 58-kD kinase in both the in-gel autophosphorylation (a) and histone-phosphorylating activity (b) assays. Ca2+ or EGTA to a final concentration of 2 mm was added to the microsomal proteins dissolved in SDS-PAGE sample buffer. After SDS-PAGE, the in-gel phosphorylation assays were done in the presence of Ca2+. −Ca2+ and +Ca2+ indicate the absence and presence of Ca2+ in the SDS-PAGE sample buffer, respectively. C, Ca2+ dependence of the in-gel autophosphorylation (indicated by 58-kD with arrow) and in vitro activity (columnar figures) of the kinase in a medium pH at 7.5 and in the presence of Mg2+ at 10 mm and EGTA at 0.45 mm. The in vitro and in-gel histone III-S-phosphorylating activities and the in-gel autophosphorylation of the kinase were assayed as described in “Materials and Methods.” Values in the columnar figures are means ± se (n = 5). D, The same assay as in C but in different concentrations of Mg2+ and in the presence of 0.55 mm Ca2+. E, The same assay as in C but in different medium pHs and in the presence of 0.55 mm Ca2+ and 10 mm Mg2+. F, Inhibition of both the in-gel autophosphorylation (indicated by 58-kD autophosph) and histone-phosphorylating activity (indicated by 58-kD histone phosph) of the 58-kD kinase by CaM antagonists or kinase inhibitors. CaM was used at 5 μm; TFP or W5 at 250 μm; W7 at 100 (W7*) or 250 μm (W7**), and K252a at 10 μm. These reagents were added, respectively, to the phosphorylation reaction medium (buffer B as described in “Materials and Methods”) for a preincubation and a subsequent reaction incubation for 32P-labeling to the kinase or its substrate histone as described in “Materials and Methods;” − and + indicate the absence and presence of Ca2+ in the reaction buffer, respectively.