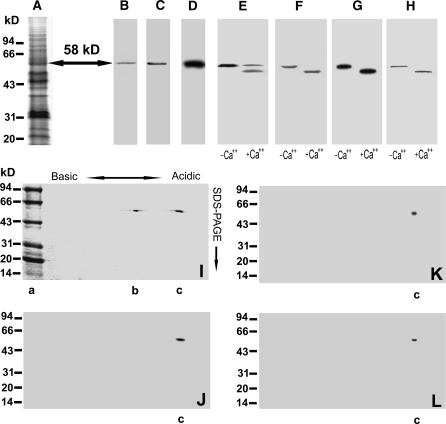
Figure 4.
Purification of the ACPK1 kinase. The portions at the 58-kD point (arrow) of SDS-polyacrylamide gels (A, Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-252-stained gels) were excised, crushed, and eluted for purification of 58-kD proteins as described in “Materials and Methods.” The collected 58-kD proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE (B, Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-252-stained gels), immunorecognized by anti-soybean CDPKα serum (C), and detected by in-gel autophosphorylation assay (D). The purified 58-kD proteins were further analyzed for their Ca2+-dependent electrophoretic mobility shift with the assays of SDS-PAGE (E, Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-252-stained gels), in-gel phosphorylation (F), histone-phosphorylating activity (G), and immunoblotting by anti-soybean CDPKα serum (H). IEF/SDS-PAGE two-dimensional electrophoresis of the purified 58-kD proteins displays two polypeptides at the 58-kD point but with different pI (I, Coomassie Brilliant Blue R-252-stained gels). One of the two polypeptides (lane c in sections I–L) is shown to be the 58-kD ABA-stimulated Ca2+-dependent protein kinase with the assays of in-gel autophosphorylation (J), histone-phosphorylating activity (K), and immunoblotting by anti-ACPK1-N40 serum (see “Materials and Methods”), an antibody specific to the 58-kD ACPK1 kinase (L). The molecular masses of protein standards are shown at the left of the sections in kD. Lane a in section I shows the protein standards on gel; −Ca2+ and +Ca2+ in sections E to H indicate the absence and presence of Ca2+, respectively.