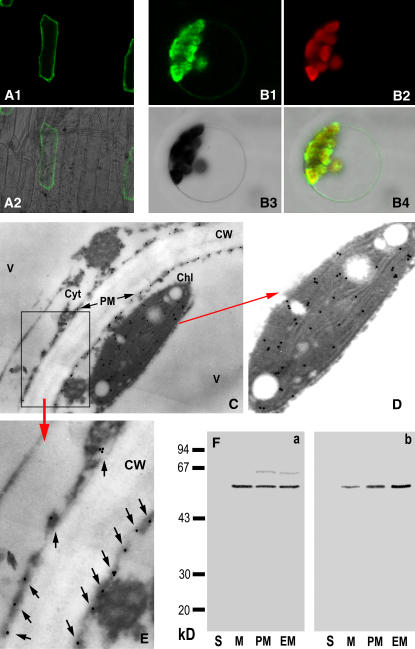
Figure 9.
Subcellular localization of ACPK1. A1 and A2, Transient expression of ACPK1-GFP fusion protein in the epidermis cells of onion. The fusion protein is present in the cell outlines, shown by the ACPK1-GFP fluorescence image (A1) and merged image (A2) of laser-scanning confocal microscopy. B1 to B4, Transient expression of ACPK1-GFP fusion protein in the protoplast of Arabidopsis shows that the fusion protein is localized in both the plasma membranes and protoplasts. The laser-scanning confocal microscopy images are the ACPK1-GFP fluorescence (B1), chlorophyll autofluorescence (B2), bright field (B3), and merged (B4) images. C, Immunogold labeling of ACPK1 in the grape berry tissue with anti-ACPK1-N40 serum (antiserum against the N-terminal 40 amino acids of ACPK1) specific to ACPK1. Immunogold particles are distributed in plasma membranes (PM) and chloroplast (Chl) but not in other cellular compartments such as cell wall (CW), cytosol (Cyt), and vacuole (V). The arrows indicate the presence of the immunogold particles along the plasma membranes. D, An amplified portion of the image C, displaying clearly the chloroplast localization of the immunogold particles representing ACPK1. E, Blow up of the boxed-in area in C. Arrows indicate the immunogold particles localized to plasma membranes. F, Immunoblotting in different subcellular fractions with either anti-ACPK1L serum (antiserum against the full-length ACPK1; a) or anti-ACPK1-N40 serum (b). The fractions of soluble portion (lanes S, 40 μg protein), microsomes (lanes M, 20 μg protein), plasma membranes (lanes PM, 20 μg protein), and endomembranes (lanes M, 20 μg protein) were separated on a 12% SDS-polyacrylamide gel and then subjected to immunoblotting. The molecular masses of protein standards are shown at the left of the sections in kD.