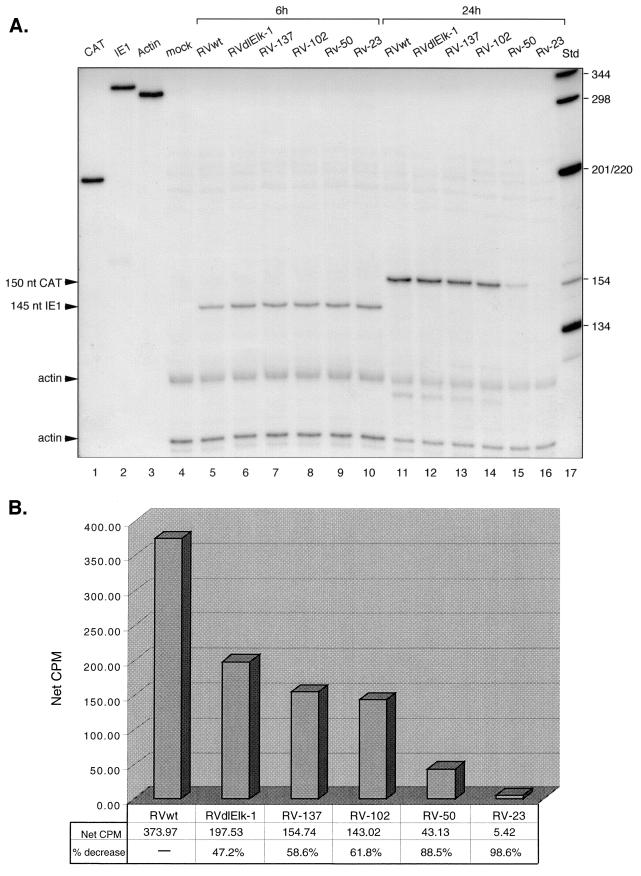
FIG. 3.
Steady-state RNA levels transcribed from the UL4-CAT promoter with either the wild type or various mutations at early times after infection. Cytoplasmic RNA was isolated at the indicated time points after HFFs were infected with RVwt, RVdlElk-1, RV-137, RV-102, RV-50, or RV-23 at approximately 5 PFU/cell and then subjected to the RNase protection assay as described in Materials and Methods. (A) Autoradiogram of RNase protection assay. Lanes: 1 to 3, 32P-labeled CAT, IE1, and actin riboprobes not treated with RNase, respectively; 4, mock infected; 5 to 10, RVwt, RVdlElk-1, RV-137, RV-102, RV-50, and RV-23 at 6 hpi, respectively; 11 to 16, RVwt, RVdlElk-1, RV-137, RV-102, RV-50, and RV-23 at 24 hpi, respectively; 17, 32P-labeled DNA standard molecular weight markers (Std). For lanes 4 to 10, 150 cpm of both 32P-labeled IE1 and actin antisense probe was used. For lanes 11 to 16, 150 cpm of both 32P-labeled actin and CAT antisense probe was used. The sizes of the protected CAT and IE1 RNAs are indicated. nt, nucleotides. (B) Image acquisition analysis of steady-state levels of CAT RNA. The IE1 signal at 6 hpi or the CAT RNA signals at 24 hpi were first normalized to the corresponding actin signals. The resulting numbers were used to determine the final normalized CAT RNA signal. Net cpm, total cpm for an equal area.