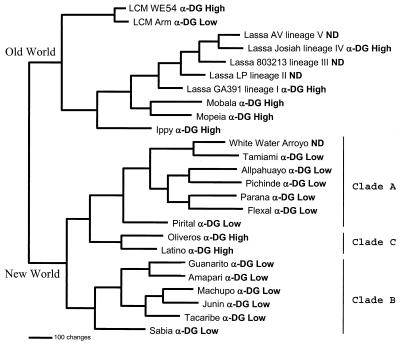
FIG. 4.
Arenavirus phylogenetic analysis. An arenavirus phylogenetic tree was generated based on maximum-parsimony analysis of the sequence differences present among an aligned 637-nucleotide region of the virus genome S segments (6, 21). Analysis using the heuristic search option and a 3:1 weighting of transversions over transitions generated a single most-parsimonious tree. Horizontal distances represent nucleotide step differences (see bar scale), while vertical branches are for visual clarity only. The arenavirus S segment sequences included the following viruses: LCMV WE54 (GenBank accession number M22017), LCM Armstrong (M20869), Lassa AV (Af246121), Lassa Josiah (J04324), Lassa 803213 (x52400), Lassa LP (af181854), Lassa GA391 (af181853), Mobala (af012530), Mopeia (m33879), Ippy (u80003), White Water Arroyo (af228063), Tamiami (u43690), Allpahuayo (ay012687), Pichinde (k02734), Parana (u43689), Flexal (u43687), Pirital (af277659), Oliveros (u34248), Latino (u43688), Guanarito (u43686), Amapari (u43685), Machupo (x62616), Junin (d10072), Tacaribe (m20304), and Sabia (u41071). Two major clades are seen, corresponding to the Old and New World arenaviruses. The New World viruses form three major clades: A, B, and C. The high- or low-affinity α-DG binding of each virus tested is indicated adjacent to the virus label. ND, not done.