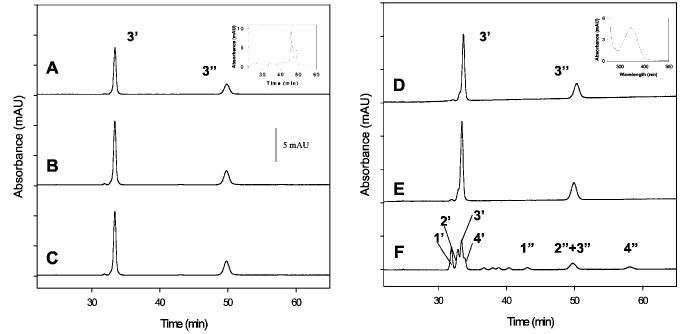
Fig. 4.
HPLC analysis of 11-cis-7-ring Rh and 11-cis-7-ring-P23H-Rh. Trace A, analysis of an isomeric composition of seven-membered locked retinals bound to Rh when added during biosynthesis. Only syn- (3′) and anti- (3″) oximes of 11-cis-7-ring retinal (isomer 3) were observed. Inset, HPLC analysis of retinoids in the cell culture after the experiment. Mainly an isomeric mixture of 7-ring retinols is present. Trace B, analysis of isomeric composition of 7-ring retinals when added during Rh biosynthesis. Rh was purified and bleached for 6 min in detergent. Trace C, analysis of the isomeric composition of seven-membered locked retinals when added during Rh biosynthesis. Rh was bleached for 20 min, and then 11-cis-retinal was added. Only 11-cis-7-ring isomer 3 is found. Trace D, same as trace A but for P23H. Inset, UV-visible spectrum of peak 3′, showing syn-oxime of 11-cis-7-ring retinal. Trace E, bleaching of 7-P23H-Rh in membranes. Trace F, isomeric chromophore composition after 7-P23H-Rh was purified and bleached for 20 min in detergent. Note that the bleaching of P23H-Rh in detergent, but not in membranes, produces all four isomers of the 7-ring- retinals. The absorbance was recorded at 325 nm.