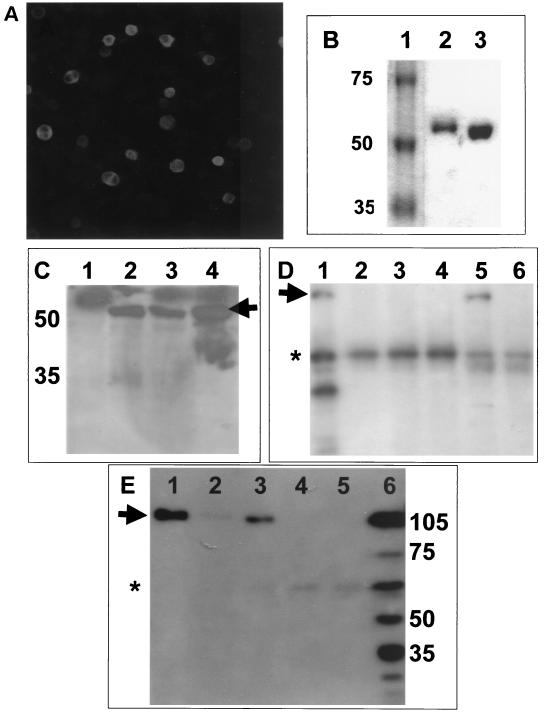
FIG. 8.
(A) Insect cells were infected with the recombinant baculovirus, BacIBVN, which expressed IBV N protein. Magnification, ×9.6. (B) Comparison of the electrophoretic mobility of recombinant His-tagged N protein purified from either Sf9 cells (lane 2) or E. coli (lane 3) by SDS-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. The molecular weight marker is shown lane 1, and the corresponding mass is shown on the left. (C) Western blot analysis with polyclonal guinea pig anti-IBV sera of Vero cells transfected with pTRiEx1.1 (lane 1), Vero cells transduced with BacIBVN (lane 2), Vero cells transfected with pTriExIBVN (lane 3), or N protein purified from insect cells infected with BACIBVN (lane 4). The positions of the molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown to the left, and the arrow indicates the position of the IBV N protein. (D) Western blot analysis of nucleolin from RNase-treated nuclear extract (lane 1); RNase-treated nuclear extract passed over NTA beads (lane 2), immobilized DcuR protein (lane 3), immobilized HIV core protein (lane 4), and immobilized phosphorylated IBV N protein (lane 5); and untreated extract passed over immobilized phosphorylated IBV N protein (lane 6). The position of mature nucleolin (∼105 kDa) is indicated by an arrow. The asterisk indicates nonspecific binding of an unidentified protein of ∼60 kDA. (E) Western blot analysis of nucleolin from RNase-treated nuclear extracts passed over immobilized phosphorylated (lane 1) and nonphosphorylated (lane 3) N protein and NTA beads (lane 5); nucleolin from untreated extracts passed over immobilized phosphorylated (lane 2); and nonphosphorylated (lane 4) N protein. Nucleolin from whole-cell lysate is shown in lane 6. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are shown to the right, and the arrow indicates the position of mature nucleolin. The asterisk indicates nonspecific binding of an unidentified protein of ∼60 kDA.