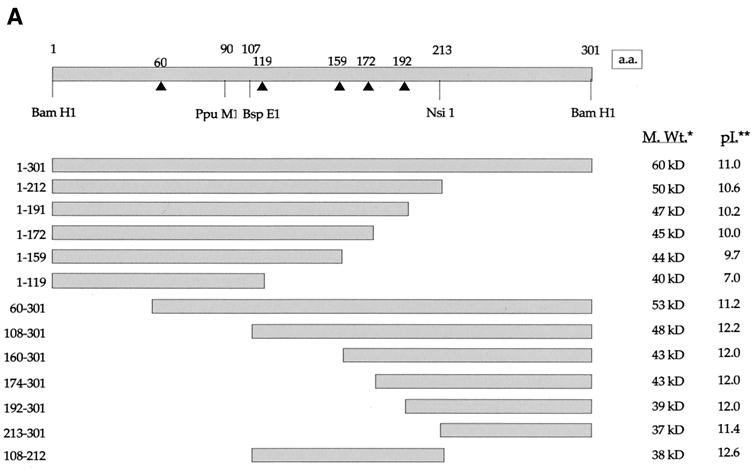
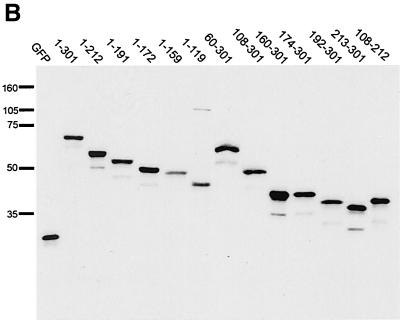
FIG. 2.
Construction and expression of VP22 truncations. (A) A range of N- and C-terminal truncations of VP22 were constructed either with restriction sites present within the VP22-encoding gene sequence (UL49) or with BglII sites introduced by insertion mutagen-esis (represented by triangles). Each truncated VP22 was fused at its N terminus to GFP to produce the panel of proteins shown. In all cases the numbers refer to amino acid (a.a.) position within the VP22 open reading frame. *, Predicted molecular size (M. Wt.) of the GFP fusion proteins. **, Predicted pI of the VP22 moiety of the fusion protein. (B) Expression vectors for the full-length and truncated VP22s, to-gether with the GFP expression vector, were all transfected into COS-1 cells, and cell extracts were analyzed by Western blotting with an anti-GFP monoclonal antibody. Note that the proteins 160-301 and 174-301 have similar molecular sizes because of the presence of an extra polylinker sequence in the 174-301 construct.