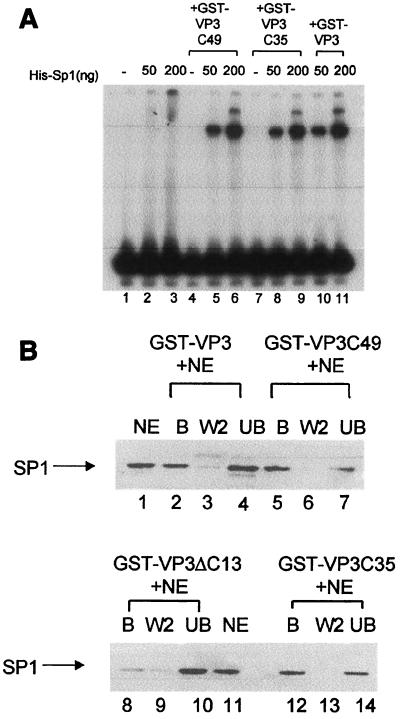
FIG. 6.
The VP3 C-terminal amino acids are sufficient for interactions with Sp1. (A) Cooperativity between Sp1 and VP3 mutants in DNA binding. A radioactively labeled six-GC-box DNA fragment (89 bp) (lane 1) was incubated with purified His-Sp1 and different VP3 mutants as indicated above the lanes. His-Sp1 produced in insect cells has lower DNA-binding activity than native Sp1; therefore, larger quantities of Sp1 were used in this experiment than in the experiment shown in Fig. 5B (50 ng of His-Sp1 ∼50 pmol). The 89-bp GC box probe produces only two bands in these assays. (B) Binding of Sp1 to VP3 mutants. GST-VP3, GST-VP3C49, and GST-VP3C35, as indicated above the lanes, all specifically interact with Sp1 present in nuclear extracts of K562 cells. The fractions—bound protein (B), wash (W), and unbound protein (UB)—were analyzed by Western blotting with anti-Sp1 antibody. Lanes 1 and 11 contain K562 nuclear extract (NE). The aliquots shown in each of the experimental lanes correspond to equivalent amounts of the input NE. GST-VP3ΔC13 does not interact with Sp1.