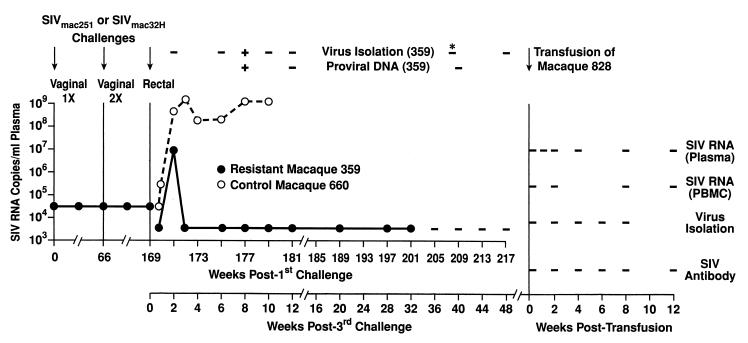
FIG. 1.
In vivo resistance of rhesus macaque 359 to mucosal SIV infection and clearance of virus. The first and second vaginal challenges and the failure of macaque 359 to become infected have been previously described in detail (7, 8). The third intrarectal exposure is detailed in Materials and Methods. SIV RNA in plasma was quantitated by nucleic acid sequence-based amplification (47). The sensitivity of SIV RNA detection was 50,000 copies/ml during the monitoring after the first and second intravaginal challenges. Repeat assays failed to detect RNA at a level of <300 copy equivalents (54). After the third challenge, the sensitivity of detection was 5,000 copies/ml in a quantitative assay and <500 copies/ml of plasma in a qualitative assay. A negative result is indicated by a dash. Attempts to isolate virus and detect proviral DNA were carried out on PBMCs except for one sample of bone marrow, marked by an asterisk. Macaque 660 was euthanized as a result of AIDS-related complications at 11 weeks postchallenge. Blood and lymph node cells obtained from macaque 359 49 weeks after intrarectal challenge were transfused into naive macaque 828, which was then monitored for 12 weeks for evidence of viral infection.