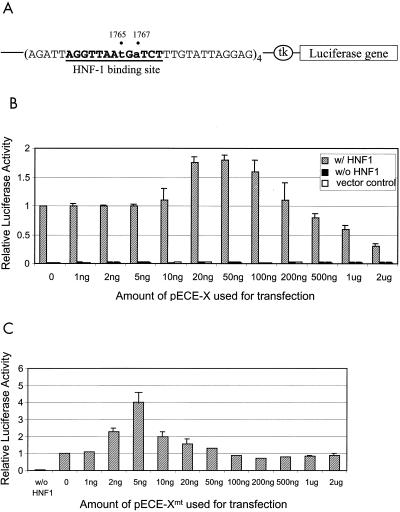
FIG. 3.
Effects of X and Xmt on the transactivation activities of HNF-1. (A) Illustration of the HNF-1 reporter construct. The luciferase reporter is boxed, and the HNF-1 binding sequence is shown in boldface letters and underlined. A minimal thymidine kinase (tk) promoter controlled the expression of the luciferase reporter. (B) Histogram of the transactivation activities of X and HNF-1. Shaded box, cotransfection of pCpHNF1-Luc and pCMV-HNF-1; solid box, transfection of pCpHNF1-Luc with pRc/CMV; empty box, transfection of the control reporter lacking the HNF-1 binding site. (C) Histogram of the transactivation activities of Xmt and HNF-1. In both B and C, 3 μg of pCMV-HNF-1 or pRc/CMV was used for the cotransfection with 4 μg of pCpHNF1-Luc or the control reporter ptk-Luc. The amount of pECE-X or pECE-Xmt used for the transfection is indicated at the bottom of the chart. In all cases, 40 ng of pXGH5, a plasmid that expressed the human growth hormone, was also used for cotransfection to monitor the transfection efficiency. All the luciferase activities expressed were normalized against the luciferase activity derived from the cotransfection of pCMV-HNF-1, pCpHNF1-Luc, and pECE-1. The results represent the averages of at least three independent experiments.