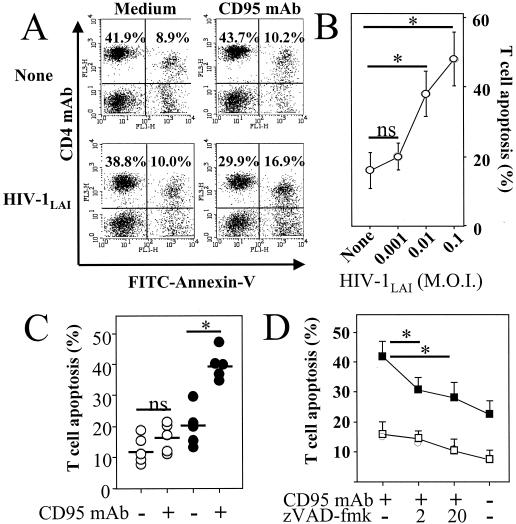
FIG. 2.
HIV-1LAI-mediated priming of CD4+ T cells for CD95-induced death. (A) PBMC were incubated for 2 h in the absence (None) or presence of HIV-1LAI (MOI of 0.01), and cells were washed and incubated for 4 days in medium alone (Medium) or in the presence of an agonistic CD95 MAb (1 μg/ml) (CD95 MAb). Numbers indicate percentages in each quadrant. Dying CD4+ T cells were assessed by two-color flow cytometry, with PC5-labeled CD4 MAb and FITC-labeled annexin V. (B) The percentage of dying CD4+ T cells was calculated as follows: [CD4+ annexin+/(CD4+ annexin+ + CD4+ annexin−)] × 100. Results are the means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was assessed by Student's t test (∗, P < 0.05; ns, no significant statistical difference). (C) Purified CD4+ T cells were incubated for 2 h in the absence (○) or presence (•) of HIV-1LAI (MOI of 0.01) and then washed and incubated for 4 days in medium alone (−) or in the presence (+) of an agonistic CD95 IgM MAb (1 μg/ml). Percentages of dying CD4+ T cells were assessed by two-color flow cytometry, with CD4 MAb and annexin V, and were calculated as follows: [CD4+ annexin+/(CD4+ annexin+ + CD4+ annexin−)] × 100. Each symbol represents one individual donor, and bars represent mean values in each group. Statistical significance was assessed by Student's t test (∗, P < 0.05; ns, no significant statistical difference). (D) Caspase inhibitor decreased CD95-mediated T-cell death. CD4+ T cells were incubated for 2 h in the absence (□) or presence (▪) of HIV-1LAI (MOI of 0.01) and then washed and further incubated in medium alone for 4 days. CD4+ T cells were then further incubated for 18 h in the absence (−) or presence (+) of 1 μg of agonistic anti-CD95 (CD95 MAb) per ml and in the absence (−) or presence (+) of a 2 μM (“2”) or a 20 μM (“20”) concentration of the broad caspase inhibitor zVAD-fmk. Percentages of dying CD4+ T cells were assessed by flow cytometry with annexin V. The percentage of dying CD4+ T cells was calculated as follows: [CD4+ annexin+/(CD4+ annexin+ + CD4+ annexin−)] × 100. Results are the means ± standard deviations of three independent experiments. Statistical significance was assessed by Student's t test (∗, P < 0.05).