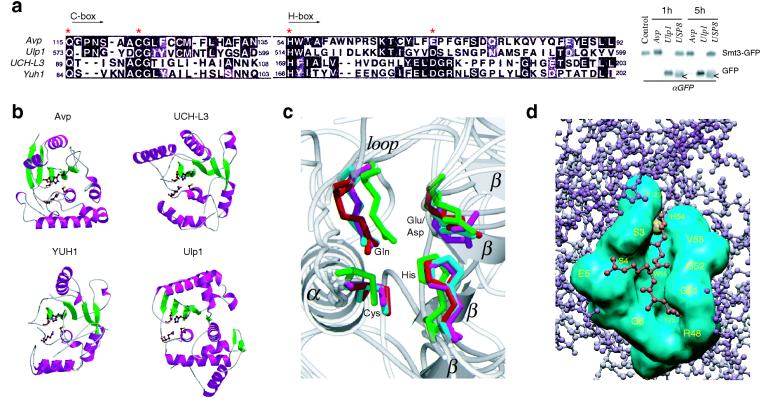
FIG. 4.
Structural comparison of Avp with UCH and Ulp families of enzymes. (a) Sequence alignment of the catalytic core domains (Cys and His boxes) of Avp, human UCH-L3, yeast YUH1, and yeast Ulp1 (MEGALIGN [6]). Asterisks indicate the residues of the catalytic triad and Gln residue of the oxyanion hole. Western blot shows the comparative cleavage of Smt3-GFP fusion by Avp, Ulp1, and deubiqutinating enzyme USP8. White arrows show the protein present in crude USP8 preparation cross-reacting with anti-GFP antibody. (b) Ribbon diagrams of the peptidases (PDB identifiers 1AVP, 1UCH, 1CMX, 1EUV). The side chains of the catalytic residues and Gln residue of the oxyanion hole are shown. Figure 4b and c were prepared with MOLSCRIPT (19) and RASTER3D (27). (c) Comparison of the peptidase active sites. Superposition of the active site residues, obtained with the program LSQMAN (CCP4 suite [4]). Avp is shown in magenta, UCH-L3 s shown in green, YUH1 s shown in cyan, and Ulp1 s shown in red. Secondary structure elements of Avp are labeled. (d) Model of the binding of ubiquitin C-terminal peptide LRG-Glz (red) to the active-site cleft of Avp (cyan). The active site tetrads of Avp and YUH1 (in the complex with Ubal) were aligned, and the residues involved in Ubal binding by Avp were identified by determination of the contacts between LRG-Glz peptide and Avp (CCONTACT, CCP4 suite [4]).