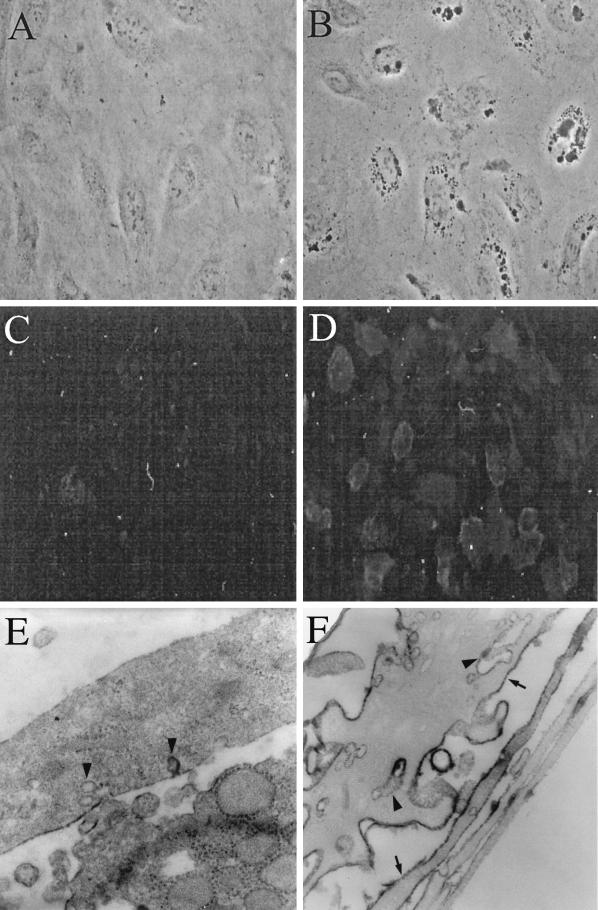
FIG. 5.
HIV-1 exposure of BMVECs induces ICAM-1 on plasma membranes and in cytoplasmic vacuoles. BMVECs, sham inoculated or inoculated with HIV-1 at a multiplicity of 105 RNA copies per cell, were fixed at the indicated times and examined by phase-contrast, fluorescence, or electron microscopy. (A) Control BMVECs show no cytoplasmic vacuoles (3 h post-sham infection; phase-contrast microscopy; magnification, ×100). (B) Virus-exposed BMVECs display cytoplasmic vacuoles (3 h p.i.; phase-contrast microscopy; magnification, ×100). (C) Control BMVECs display no ICAM-1 (24 h p.i.; anti-ICAM immunofluorescence; magnification, ×40). (D) HIV-1-exposed BMVECs strongly display ICAM-1 on the plasma membrane (24 h p.i.; anti-ICAM immunofluorescence; magnification, ×40). (E) Control BMVECs show no or weak ICAM-1 horseradish peroxidase (HRP) reaction product on the plasma membrane (arrowheads) (3 h post-sham infection; IEM with anti-ICAM-1; magnification, ×17,000). (F) Virus-exposed BMVECs display strong ICAM-1 HRP reaction product on the plasma membrane (arrows) and within vesiculocanalicular cytoplasmic structures (arrowheads) (3 h p.i.; IEM with anti-ICAM-1; magnification, ×17,000).