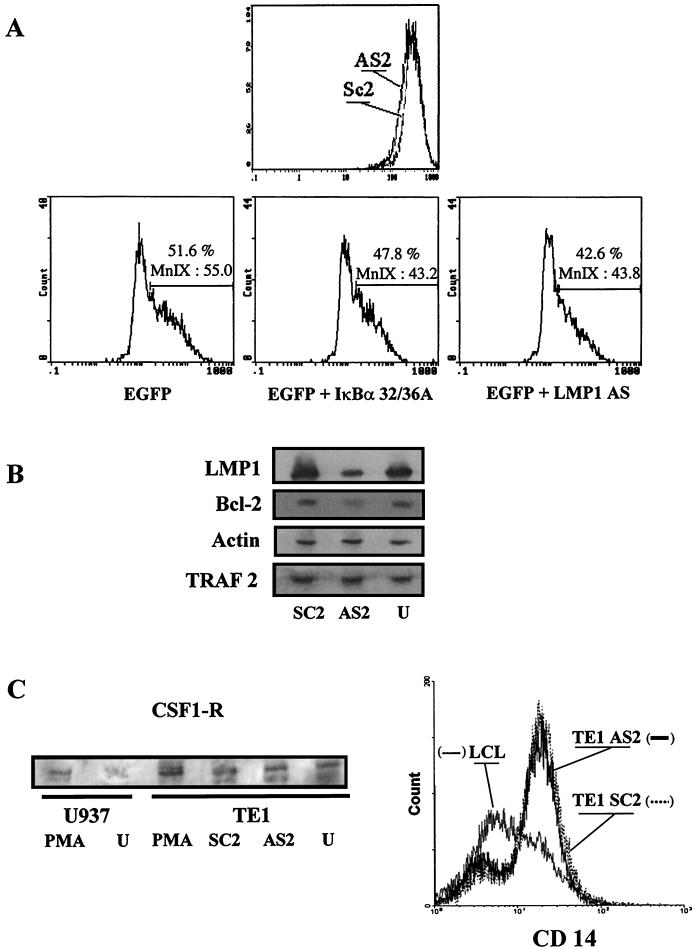
FIG. 8.
Effect of LMP-1 inhibition on expression of different markers in E1 or TE1 cells. (A) Effect on ICAM-1/CD54 expression on E1 cells analyzed by flow cytometry. (Top) The LMP-1 antisense oligonucleotide (AS2) down-regulated membrane expression of LMP-1 molecular target ICAM-1 on E1 cells. Scramble oligomers were used as the control (SC2). (Bottom) The same results were obtained with cells cotransfected with pEGFP-C1 and pSV LMP-1-AS or with pcDNA3 containing the coding sequence for mutated IκBα32/36A. The percentage of ICAM-1-expressing cells and the density of expression (MnI X) in these conditions are indicated. (B) Western blot analysis of several markers after LMP-1 inhibition experiments with TE1 cells. Immunoblots were probed with the S12 monoclonal antibody (LMP-1) or antibodies specific for TRAF-2, BCL-2, and actin proteins. Detection was performed after antisense oligonucleotide (AS2) or scramble (SC2) treatment, and results were compared to those for untreated cells (U). (C) Western blot and cytometry analyses of monocytic markers. (Left) Detection of CSF1-R after AS2, SC2, or PMA treatment in TE1 cells. U937 cells untreated or stimulated by PMA were used as the control for CSF1-R induction. (Right) Flow cytometry profile for CD14 labeling after treatment of TE1 cells. Rafa B-LCL is shown as a negative control.