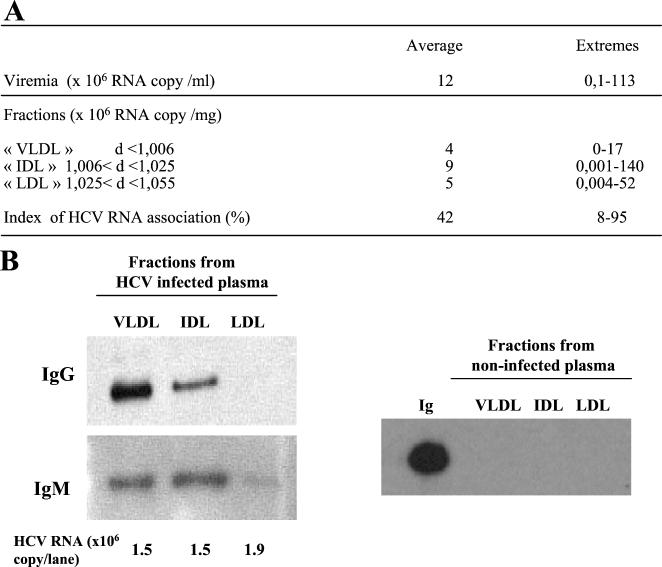
FIG. 1.
Characterization of HCV RNA-containing particles in very-low- to low-density plasma fractions. (A) Serum and three plasma fractions corresponding to VLDL, IDL, and LDL were prepared from 27 chronically HCV-infected patients. The HCV genotype distribution was as follows: 1 genotype 1a, 15 genotype 1b, 1 genotype 2b, 5 genotype 3a, 5 genotype 4, and 3 ambiguous genotypes. Viremia was calculated as the number of HCV RNA copies per milliliter of serum. Viral loads in fractions were calculated as the number of HCV RNA copies per milligram of protein. The association of HCV RNA with low-density fractions is expressed as an index as described in Materials and Methods. d, density of fraction. (B) Fractions from infected and noninfected plasma samples were analyzed for the presence of immunoglobulins (Ig). Five-microgram quantities of fractions corresponding to VLDL, IDL, and LDL were separated by SDS-10% PAGE and transferred to PVDF membranes for IgG and IgM detection. A positive control experiment was performed by running 200 ng of purified IgG in the gel.