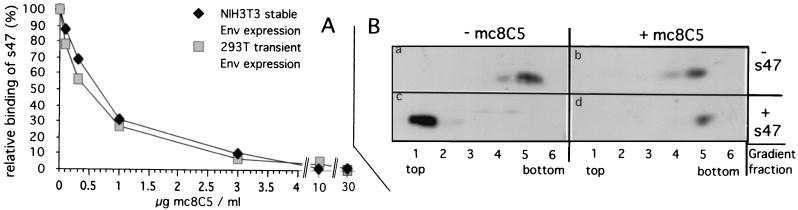
FIG. 4.
Binding of the Tva receptor peptide, s47, to EnvA on the cell surface (A), as well as s47-induced liposome binding of a soluble EnvA (B), is inhibited by mc8C5-4. (A) For flow cytometry analysis of s47 binding, cells expressing EnvA either stably (NIH 3T3) or transiently from plasmid pCB6-EnvA (293T) were suspended and preincubated on ice with mc8C5-4 antibody at the indicated concentrations. Biotinylated s47 was added, and after incubation on ice and washes, Tva peptide that had bound to EnvA was reacted with avidin-Oregon green 488. Cells were then fixed in PFA, and the fluorescence intensity of Oregon green 488 as a measure of the (relative) amount of s47 bound to cells was quantitated. (B) Liposome flotation assay. A soluble form of EnvA (which includes the fusion subunit ectodomain of TM [gp37]) was incubated in PBS with or without mc8C5-4 prior to addition of s47 or PBS. The formation of EnvA-s47 complexes able to interact with liposomes was probed by sucrose gradient centrifugation as described in Materials and Methods. Six fractions were taken from the top (fraction 1) to the bottom (fraction 6) of the gradient and probed by Western blotting with an antibody which recognizes gp37. Env proteins associated with liposomes are expected to float to the top of the gradient.